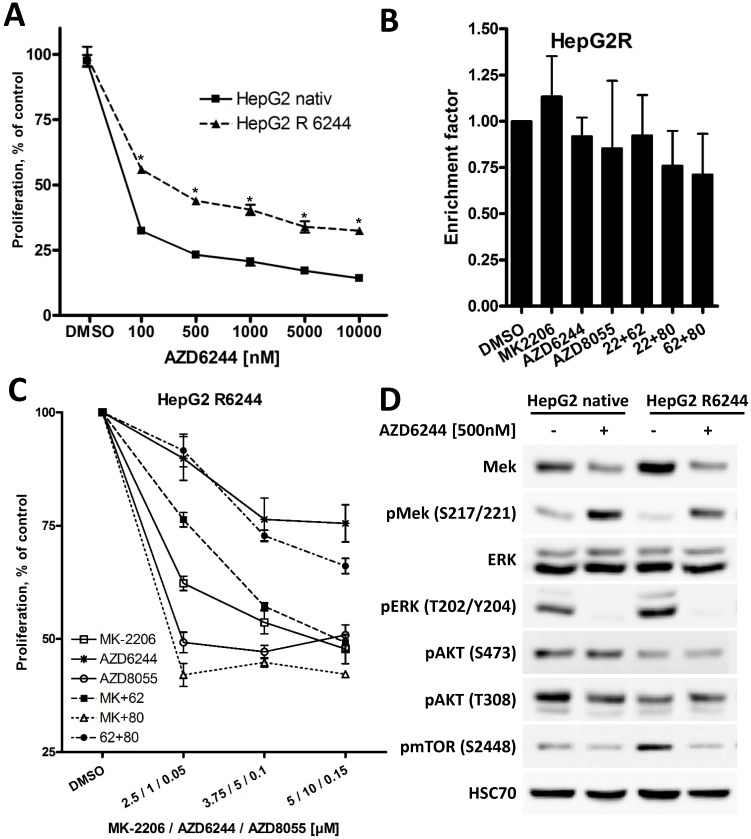
Figure 6.
Long term exposure of HepG2 cell to AZD6244 results in acquired resistance. (A) HepG2 and AZD6244 resistant HepG2R cells were seeded into 96-well plates and treated with increasing concentrations of AZD6244, controls were treated with DMSO. Proliferation was analyzed after 72h by BrdU incorporation. Each data point represents three independent experiments, each performed in triplicates. Bars: SD; *, p < 0.05. (B) HepG2R cells were treated with 2 µM MK-2206, 1 µM AZD6244, 75 nM AZD8055, or a combination of two of compounds as indicated for 24h, and induction of apoptosis compared to untreated cells was determined using the Cell Death Detection ELISA kit. No significant induction of apoptosis was observed in any experimental condition in HepG2R cells. (C) HepG2R cells were seeded into 96-well plates and treated with the indicated compounds or their combinations. Proliferation was analyzed after 72h by BrdU incorporation. Each data point represents mean of three independent experiments. Bars: SD. (D) HepG2R cells were treated with 500nM AZD6244 or DMSO. PI3K/AKT/mTOR and RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway activity was analyzed by Western blot. HSC70 served as loading control.