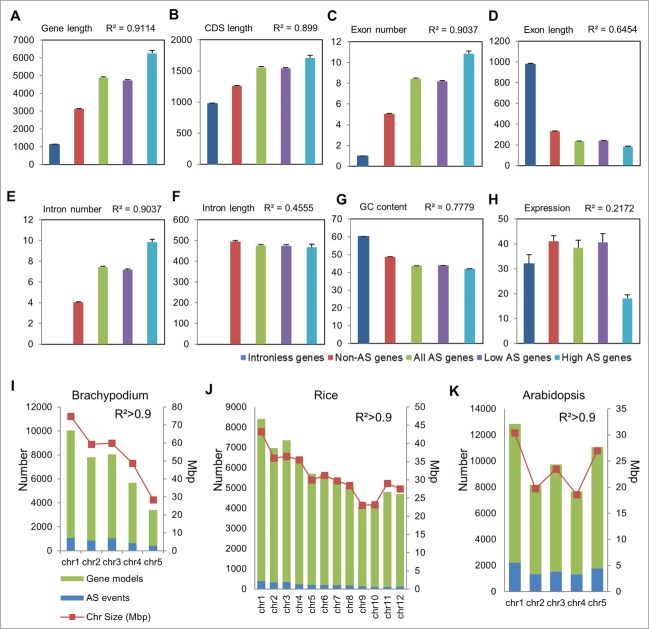
Figure 1.
Genomic attributes of intronless, constitutively- and alternatively-spliced genes and relationship with splicing incidence and frequency. (A) Gene length [bp] (B) CDS length [bp] (C) exon number, (D) exon length [bp], (E) intron number, (F) intron length [bp] (G) %GC content, and (H) expression [Fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped fragments, FPKM] statistics of intronless genes, constitutively spliced (Non-AS) and alternatively spliced (AS) genes are graphed. Genes with <5 and ≥5 isoforms are designated as low and high AS genes respectively. Pearson correlation coefficient values (R2) among the different groups are indicated. Error bars represent standard error. Statistically significant differences (α < 0.01) are determined by Tukey's Studentized Range test. AS event frequency and correlation to genome size and number of gene models per chromosome in (I) Brachypodium, (J) rice, and (K) Arabidopsis are shown. The genomic features of Brachypodium, rice and Arabidopsis were obtained from Phytozome, IGRSP, and TAIR databases, respectively.