Figure 1.
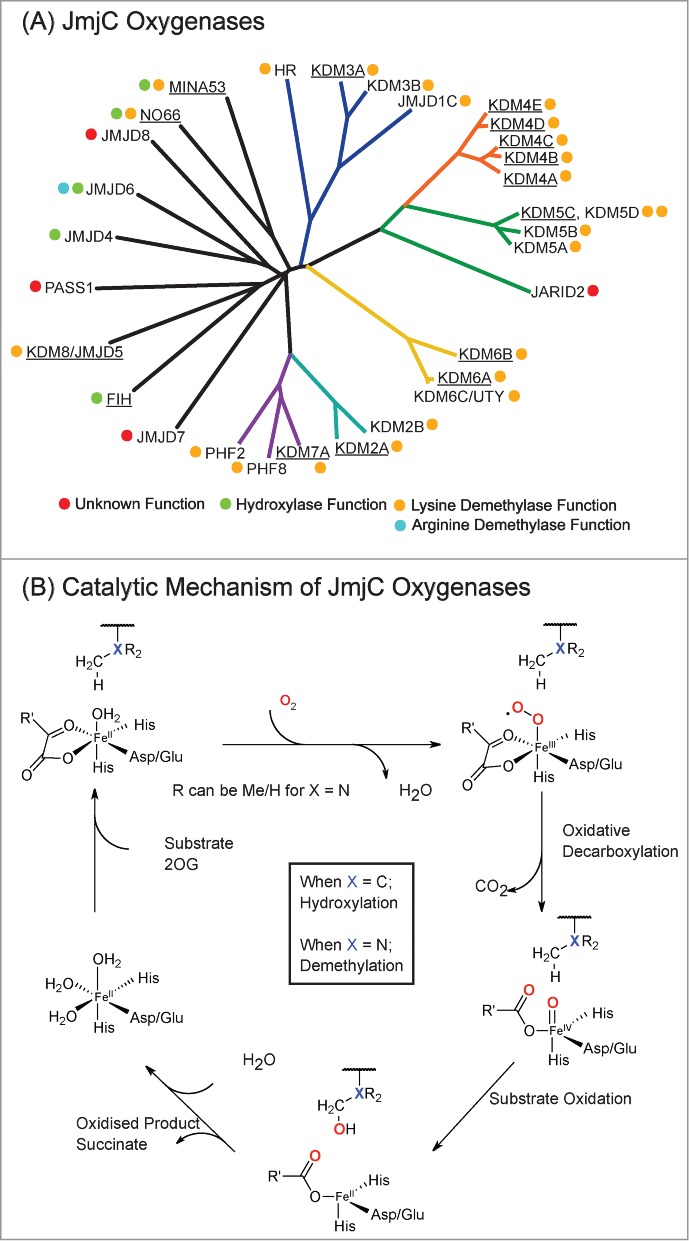
JmjC Oxygenases share sequence homology and catalytic mechanisms. (A) Phylogenetic analysis of the catalytic domains of human JmjC oxygenases. Reported catalytic functions are indicated by colored circles. MINA53, NO66 and JMJD6 have been reported to be demethylases but have subsequently been shown to have hydroxylase activities.4-6,8,9 KDM6C (UTY) was recently identified as a histone demethylase in vitro, acting on H3 peptide fragments methylated at H3K27.43 HR is Hairless Protein, a recently identified H3K9 demethylase.44 Enzymes used in this work are underlined. (B) Outline mechanism of JmjC oxygenase catalysis. Oxidative decarboxylation of 2-oxoglutarate (2OG) in the active site forms a highly reactive iron(IV)-oxo intermediate, which hydroxylates the substrate. In the case of demethylation (X = N), the hydroxylated product is unstable and fragments to produce the demethylated species and formaldehyde. The exact protonation states of water molecules complexed to the iron(II) species are unknown.
