Figure 4.
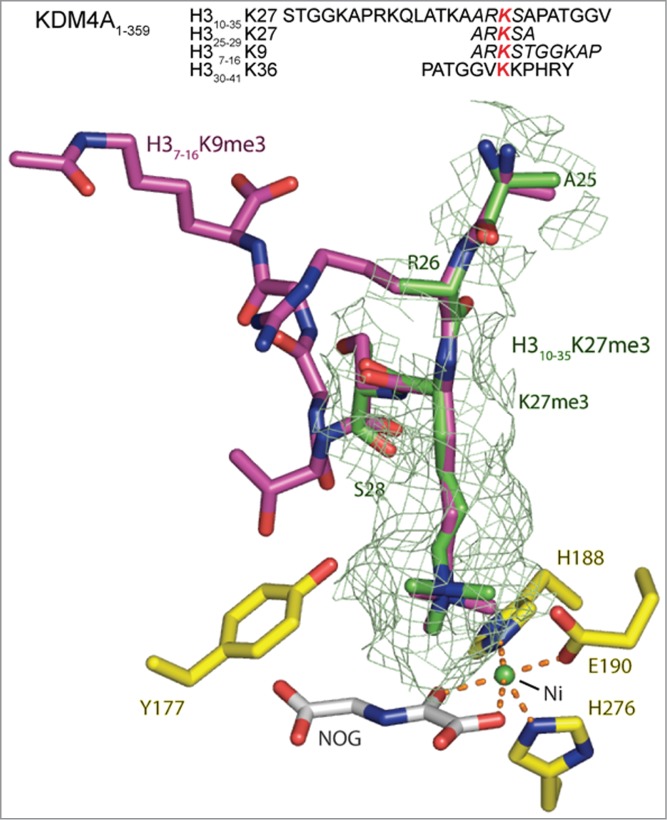
View from an X-ray crystal structure of the catalytic domain of KDM4A in complex with an H3K27me3 fragment peptide (PDB ID: 4V2W). The active site residues are highlighted in yellow. The visible residues of the 25mer H310–35K27me3 (green) peptide is shown overlaid with H3K9me3 (pink), as complexed with KDM4A (PDB ID: 2OQ6, nickel substituted for iron, and N-oxalylglycine substituted for 2OG). The position of the H3K27me3 residue of the fragment peptide correlates closely with that of H3K9me3 (and H3K36me3, Figure S18). However, in the H310–25K27me3 derived structure only the electron density for the tri-methyl lysine and the residues either side (H3R26 and H3S28) are clearly defined, suggesting the other residues are bound less tightly than the comparable H3K9 and H3K36 substrates. A second structure of a shorter 5 residue H325–29K27me3 peptide in complex with KDM4A (PDB ID: 4V2V) overlays well with that of the 25 residue peptide (Figure S19). The sequences for the H3K9, K27 and K36 peptides present in these crystal structures are included with residues for which electron density is observed in italics. The red lysine residue marks the position of the Nε-trimethylated lysine.
