Figure 1.
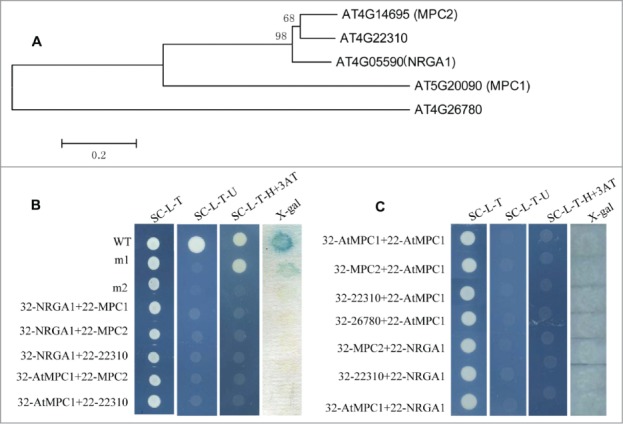
Gene structure and protein interactions in yeast. (A) Phylogenetic analysis of putative MPC proteins in Arabidopsis. The amino acid sequences of these proteins were aligned by CLUSTALX, and the phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method with the following parameters: bootstrap (replicates 1000), poisson model and complete deletion. The numbers at the nodes indicate the bootstrap values. (B) The interaction between the different MPC protein pairs. 32: pDEST32 for generation of the bait plasmid, 22: pDEST22 for construction of the prey plasmid. wt (pEXP22-RalGDS-wt), m1(pEXP22-RalGDS-m1) or m2 (pEXP22-RalGDS-m2) is control plasmid which shows strong, weak and undetectable interaction with pEXP32-Krev1, respectively. The transformed yeast cells grow on SC/-Leu-Trp (SC-L-T), SC/-Leu-Trp-Ura (SC-L-T-U), or SC/-Leu-Trp-His (SC-L-T-H) medium containing 50 mM 3-AT and aX-gal assay for β-galactosidase activity of the transformants grown on YPAD. (C) Test of protein interactions using a “swapped” 2-hybrid approach. The system is the same as shown in (B).
