Figure 3.
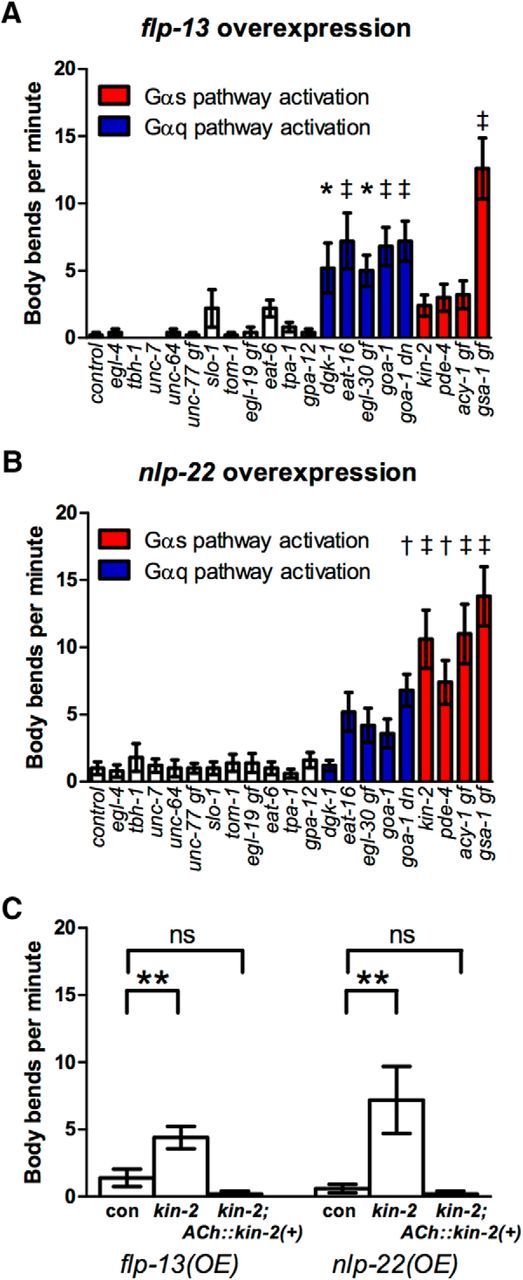
Activation of Gαq or Gαs pathways impairs locomotion quiescence caused by flp-13 or nlp-22 overexpression. A, Mutations that increase Gαq or Gαs signaling impair locomotion quiescence after flp-13 overexpression. B, Mutations that increase Gαq or Gαs signaling impair locomotion quiescence after nlp-22 overexpression. A and B, Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of body bends for 12–15 worms during a 20 s window. Each bar represents the data obtained for a different mutant strain containing the designated overexpression transgene. For detailed genotypes and data, see Table 2. gf, Gain-of-function mutation; dn, dominant-negative mutation; the others are loss-of-function mutations. Statistical significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple-comparison tests. *p < 0.05, †p < 0.01, ‡p < 0.001. C, Rescuing kin-2 function in cholinergic neurons using the unc-17 promoter rescues the effects of the kin-2 mutation on locomotion quiescence after flp-13 or nlp-22 overexpression. Con, flp-13 overexpression and nlp-22 overexpression control strains NQ570 or NQ251, respectively. n = 13–15. Each bar represents mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple-comparison tests. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
