Figure 5.
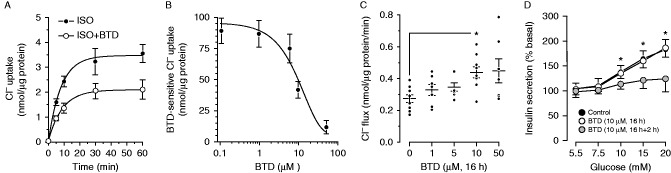
BTD-sensitive Cl− uptake and insulin secretion in MIN6 cells. (A) Cl− recovery in MIN6 depleted of intracellular Cl− under control (ISO, filled dots) or in the presence of 10 μM BTD (ISO+BTD, open dots). Cl− uptake equilibrated at basal levels after ∼15 min at room temperature and a final physiological Cl− concentration of ∼140 mM. Results are expressed as mean±s.e.m. (n=10). The initial uptake rate is approximately linear during the first 5–10 min of the reaction. Thereafter, Cl− recovery followed a mono-exponential decay. (B) Dose-response curve of Cl− uptake in Cl−-depleted MIN6 assayed 5 min after readmission of physiological Cl− in the presence of BTD (0.1–50 μM). Results are expressed as the mean±s.e.m. (n=5). (C) Long-term effect of BTD on the initial rates of Cl− uptake in MIN6. Cells were pre-incubated 16 h with the indicated concentrations of BTD and then depleted of Cl− by incubating them in Cl−-free medium plus BTD for 1 h. Then, total Cl− content was determined 5 min after incubation in ISO media containing physiological Cl−. Results are expressed as nanomole/liter of Cl− per microgram protein per unit of time. Each dot represents a single independent determination (n=6–9, *P<0.05). (D) Effect of chronic BTD pre-treatment on glucose-induced insulin secretion. MIN6 cells were cultured 16 h in media containing 5.5 mM glucose without (Control) or with 10 μM BTD. Then, BTD-treated MIN6 cells were divided into two groups: one was further incubated 2 h in KRBH plus vehicle (open dots) and another in KRBH plus 10 μM BTD (shaded dots). Insulin secretion was related to total insulin content (insulin secretion/total insulin content) and then normalized to basal levels (n=5, *P<0.05).

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a