Figure 4.
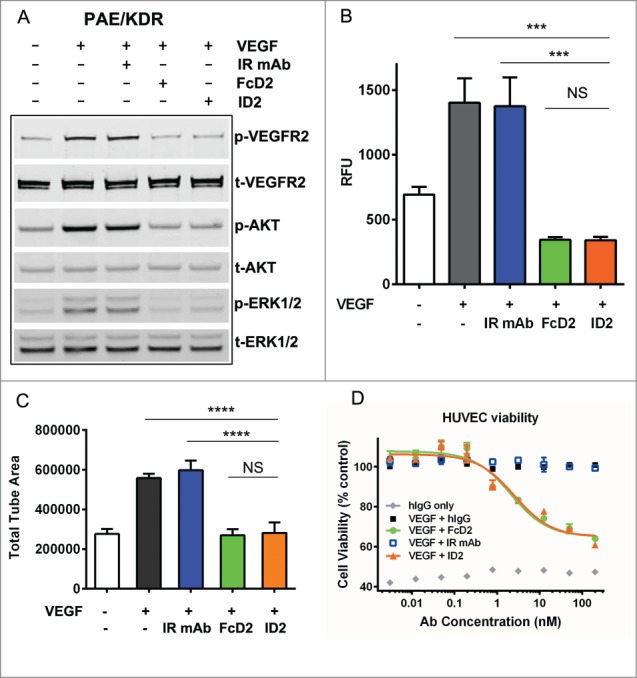
Inhibition of VEGF-mediated endothelial cell signaling and functions by ID2. (A) 100 nM ID2 inhibits VEGF-induced phosphorylation of VEGFR2, downstream AKT and ERK1/2 in PAE/KDR cells as assessed by immunoblotting analysis. IR mAb and FcD2 were used as controls. (B) In an Oris cell migration assay, PAE/KDR cells stimulated with 100 ng/ml VEGF were treated with 100 nM ID2, IR mAb, or FcD2 for 20 hours. The fluorescence intensity of migrated cells in relative fluorescence units (RFU) was measured. ID2 significantly reduced the migration compared to VEGF and IR mAb controls (p = 0.002 and p = 0.003, respectively, one way ANOVA). (C) ID2 inhibits VEGF stimulated cord formation in an ADSC/ECFC co-culture system. The total tube area for each treatment was calculated. ID2 significantly reduced the total tube area compared with VEGF only and IR mAb controls (p < 0.0001 and p < 0.0001, respectively, one way ANOVA). (D) ID2 inhibits human VEGF induced HUVEC viability in a dose dependent manner in a CellTiter Glo assay. The error bar from panels B, C and D represents the SEM from each triplicate measurement.
