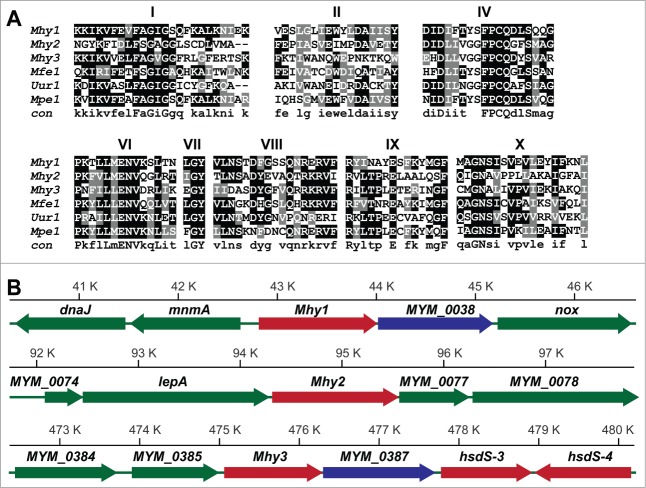
Figure 1.
M. hyorhinis MTases. (A) conserved motifs in M. hyorhinis MTases. The amino acid sequence alignment of M. hyorhinis Mhy1, Mhy2 and Mhy3, Mfe1 from M. fermentans, Uur1 from Ureaplasma urealyticus and Mpe1 from M. penetrans. Conserved motifs are indicated by numbers. A consensus sequence is shown at the bottom. (B) MTase loci in M. hyorhinis genomes. Positions of the Mhy1 (40.5–46.5 kb), Mhy2 (92–98 kb), and Mhy3 (472.5–480 kb) genes in M. hyorhinis chromosome. Genes are: dnaJ, chaperone protein; mnmA, tRNA-specific 2-thiouridylase; Mhy1, CG-specific MTase; MYM_0038, hypothetical protein; nox, NADH oxidase; MYM_0074, hypothetical protein; lepA, GTP-binding protein; Mhy2, CG-specific MTase; MYM_0077, hypothetical protein; MYM_0078, ATP-binding ABC transporter; MYM_0384, putative endonuclease or phosphatase; MYM_0385, glutamyl aminopeptidase; Mhy3, GATC-specific MTase; MYM_0387, hypothetical protein; hsdS-3 and hsdS-4, type I DNA MTases. Genes are shown as solid color bars. The direction of transcription is indicated by arrows. Putative MTase and endonuclease genes are red and blue, respectively. Other genes are green.