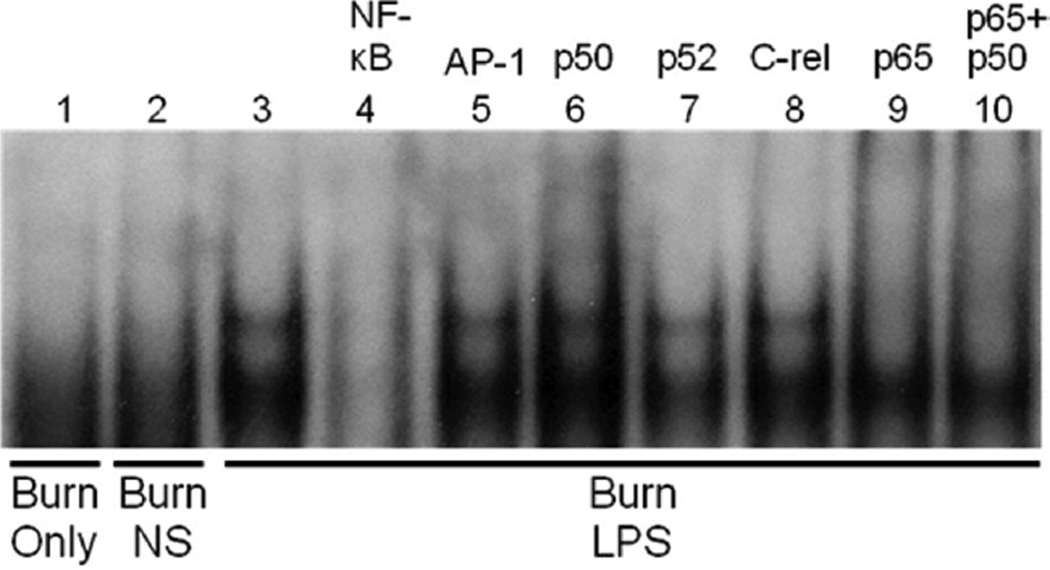
Figure 5.
Supershift electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) characterization of LPS inducible nuclear factor (NF)-κB binding in the jejunum of mice 20 minutes after LPS injection. The activation (upper) band is not present after burn injury alone or after normal saline (NS) vehicle injection (lanes 1–3). Cold competition with NF-κB but not with activated protein (AP)-1 oligonucleotide inhibited binding, demonstrating probe specificity (lanes 4 and 5). Supershift EMSA using specific antibodies directed toward p50, p52, crel, and p65 subunits show that the upper activation band is composed of p65 and p50/p65 components (lanes 6–10). The experiment was performed in triplicate to ensure reproducibility.