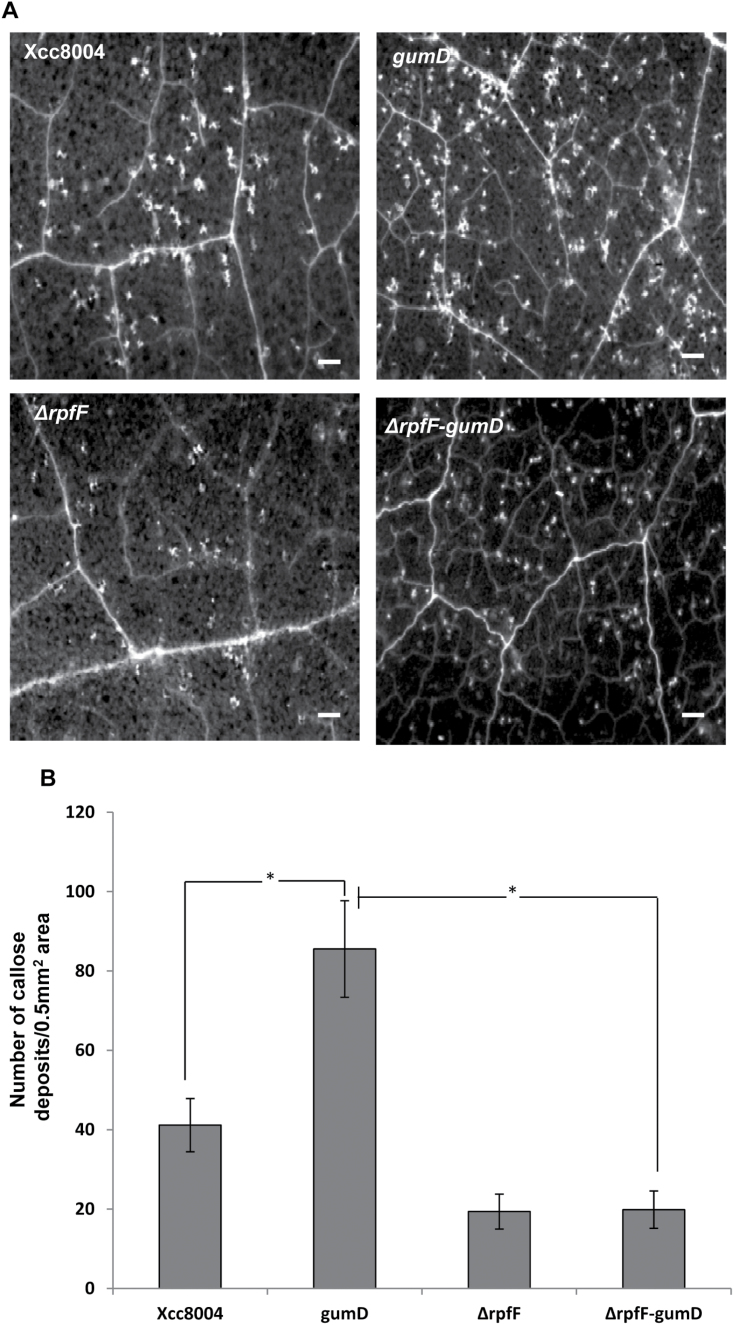
Fig. 7.
Callose deposition induced by different strains of Xcc. (A) N. benthamiana leaves were infiltrated with a 1×106 cfu ml–1 suspension of different Xcc strains; Xcc8004 (wild type), gumD (xanthan-deficient mutant), ΔrpfF (DSF-deficient rpfF deletion mutant), and the ΔrpfF-gumD double mutant. Callose deposition was visualized by staining with aniline blue and examined using a stereo fluorescence microscope 24h post-inoculation. White dots in these pictures are indicative of callose deposition. Scale bars=500 μm. (B) Average number of callose deposits per 0.5mm2 area. Error bars represent SD values from three leaves of each plant and three independent experiments. Six microscopic fields from each leaf were analysed. * indicates (P<0.001) significantly different callose deposits induced by the Xcc gumD mutant compared with either the wild-type Xcc8004 strain or the ΔrpfF-gumD double mutant as determined by two-tailed Student’s t-test.