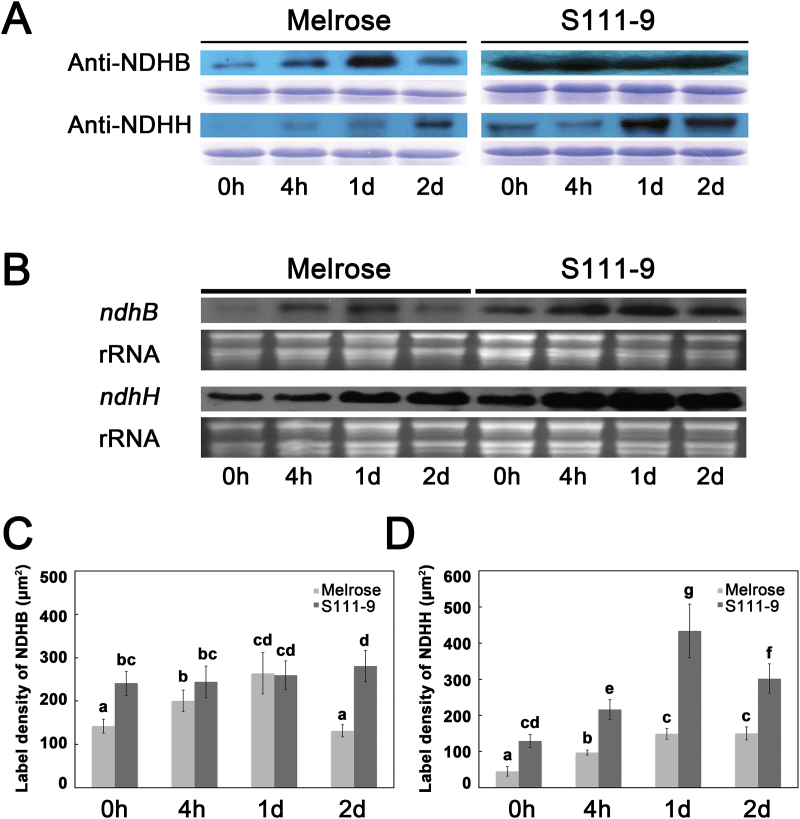
Fig. 5.
Effect of salt stress on the protein and mRNA abundance of ndhB and ndhH. (A) Changes in NDH-H and NDH-B content were analysed using immunoblotting in the leaves of Melrose and S111-9 treated with 150mM NaCl for 0h, 4h, 1 d, and 2 d. Equal loading is shown by Coomassie-stained gels below each blot. (B) Effect of salt stress on the mRNA expression of ndhB and ndhH. RNA gel blotting hybridization analysis of ndhB and ndhH was performed using the total RNA from Melrose and S111-9 treated with 150mM NaCl stress for 0h, 4h, 1d, and 2 d. The RNA samples loaded were visualized by ethidium bromide staining of 28S rRNA (lower panel). (C and D) Immunogold labelling of NDH-B and NDH-H in the chloroplast organelles of the mature leaves of soybean (Glycine max) under 150mM salt stress. Seven to eight individual cells of palisade and spongy layers were examined in several immunolabelled sections. Numbers of gold particles per unit area (μm2) are given as mean ±SD. (C) Effect of salt stress on label density of NDH-B (μm2). (D) Effect of salt stress on label density of NDH-H (μm2). Different letters indicate significantly different values (P<0.05) by Tukey’s test.