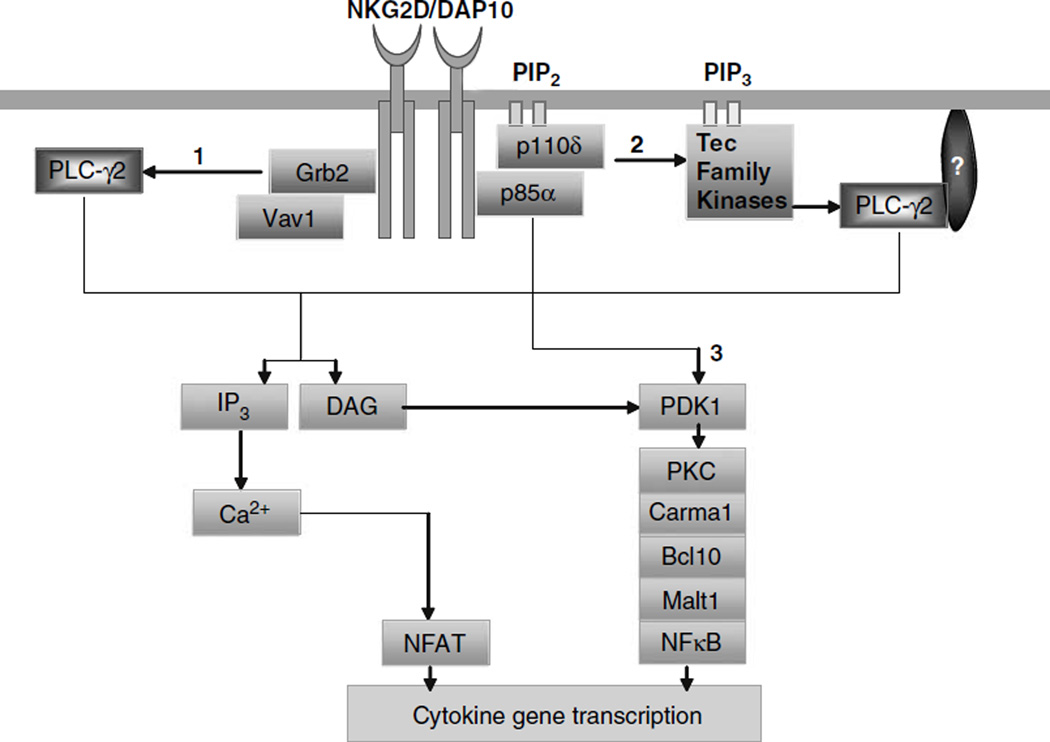
Figure 7.
Signaling pathways that are potentially regulated by p85α in the generation of cytokines. We propose that p85α can regulate cytokine gene transcriptions by: (1) a direct recruitment of PLCγ2 by Grb2/Vav-1 complexes. Grb2 is an adapter protein that binds to DAP10 through the YINM motif. Activation and recruitment of Grb2 to NKG2D/DAP10 complexes has been shown to initiate phosphorylation of PLCγ2.70 PLCγ is one of the major regulators of protein kinase C (PKC) by DAG. Thus, DAP10/p85α/Grb2-Vav1 complexes can signal either through Carma1/Bcl10/Malt-1/nuclear factor (NF)-κB or PLCγ2/IP3/Ca2+/NFAT, which lead to cytokine gene transcriptions. (2) Activation of PLCγ2 by phosphotidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) by Tec kinases. Btk is a Tec family protein tyrosine kinase, which can bind to PI3K product, PtdIns-3,4,5-P3 leading to the recruitment and phosphorylation of PLCγ2.26 This in turn can also result in the activation of PKC and Carma1/ Bcl10/Malt-1/NF-κB or PLCγ2/IP3/Ca2+/NFAT signaling pathways. (3) Direct link between PI3K and Carma1/Bcl10/Malt-1/NF-κB signaling axis. Recent studies have shown that PI3K-dependent kinase, PDK1, has the ability to activate PKC.71 Thus, the activation of PKC can link the Carma1/Bcl10/Malt-1/NF-κB signaling axis to PI3K.