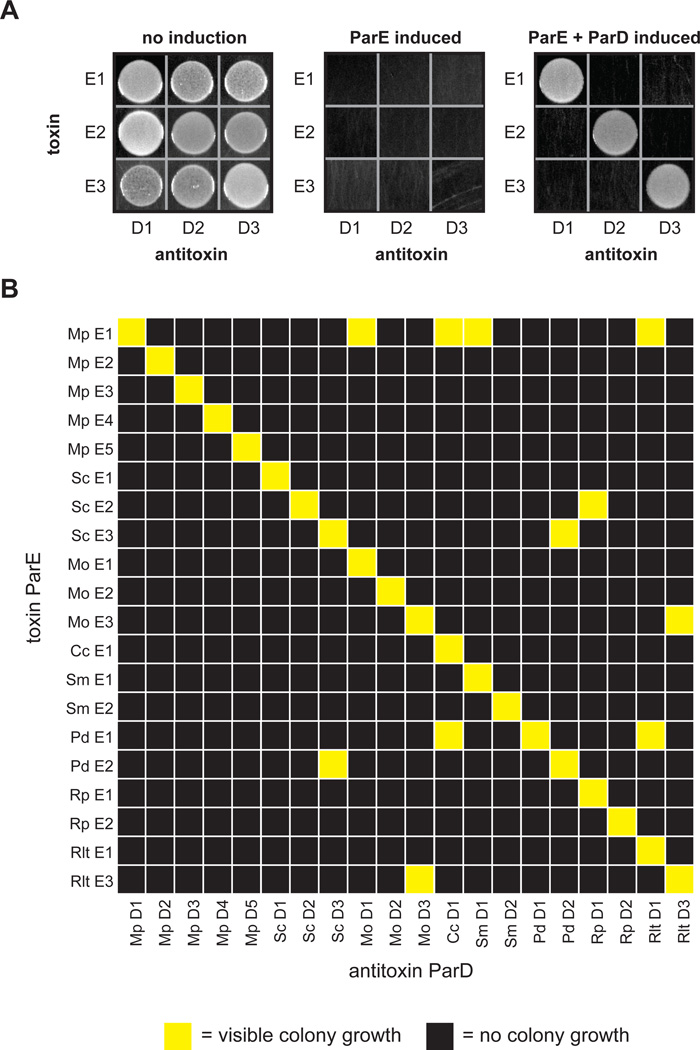
Figure 2. Toxins and antitoxins from the ParD-ParE family exhibit high interaction specificity.
(A) Testing of interaction specificity for ParD antitoxins and ParE toxins from Mesorhizobium opportunistum. Plasmids harboring the toxins and antitoxins indicated were cotransformed into E. coli with ParD and ParE induced as indicated.
(B) Comprehensive testing of interaction specificity for 20 ParD and ParE pairs from eight different species. Cells containing each possible ParD-ParE pair were grown on plates that induce the toxin and antitoxin, respectively, and grown overnight at 37°C. Yellow, visible colonies following serial dilution; black, no visible colonies.
Also see Fig. S1.