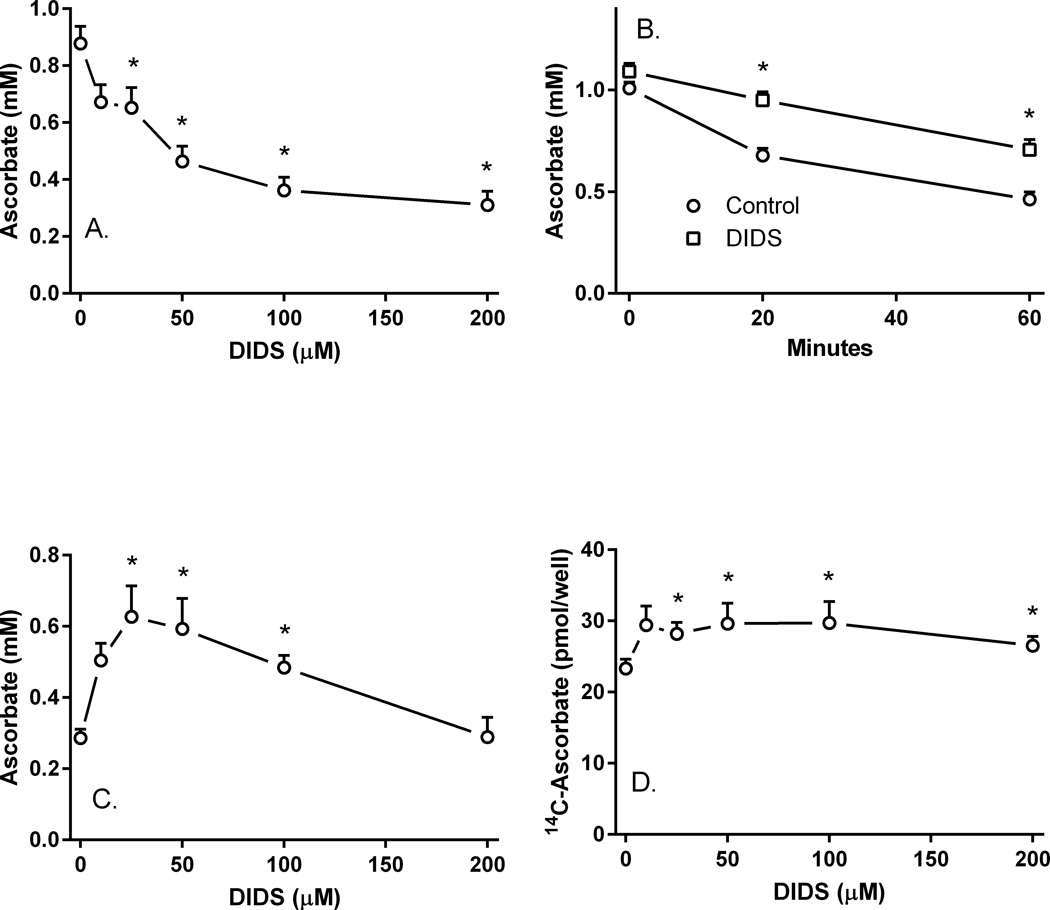
Figure 5. DIDS inhibition of ascorbate uptake and efflux.
Panel A. Pericytes were rinsed and treated in KRH containing 5 mM D-glucose with the indicated concentrations of DIDS at 37°C for 30 min before rinsing and assay of intracellular ascorbate. Results are from 6 experiments, with an “*” indicating p < 0.05 compared to a sample not treated with DIDS. Panel B. Pericytes loaded with 100 µM unlabeled ascorbate for 60 min in culture medium at 37°C were rinsed twice in 37°C glucose-KRH and treated without (circles) or with (squares) 100 µM DIDS in 1 ml of glucose-KRH. At the indicated times, the medium was aspirated and the cells were rinsed twice in 2 ml of ice-cold KRH before assay of intracellular ascorbate. Results are from 5 experiments, with an “*” indicating p < 0.05 compared to the sample not treated with DIDS at the same time point. Panel C. Pericytes were loaded with 100 µM unlabeled ascorbate for 60 min, rinsed twice in glucose-KRH, and treated in 37 °C glucose-KRH with the indicated concentration of DIDS. After 30 min, the cells were rinsed again in ice-cold KRH and taken for assay of intracellular ascorbate. Results are shown from 6 experiments with an “*” indicating p < 0.05 compared to the sample not treated with DIDS. Panel D. Pericytes in culture medium were loaded with 10 µM radiolabeled ascorbate for 60 min, rinsed twice in glucose-KRH, and treated with the indicated concentration of DIDS in glucose-KRH. After 30 min, the cells were rinsed and taken for assay of intracellular radiolabeled ascorbate. Results are shown from 7 experiments, with an “*” indicating p < 0.05 compared to the sample not treated with DIDS.