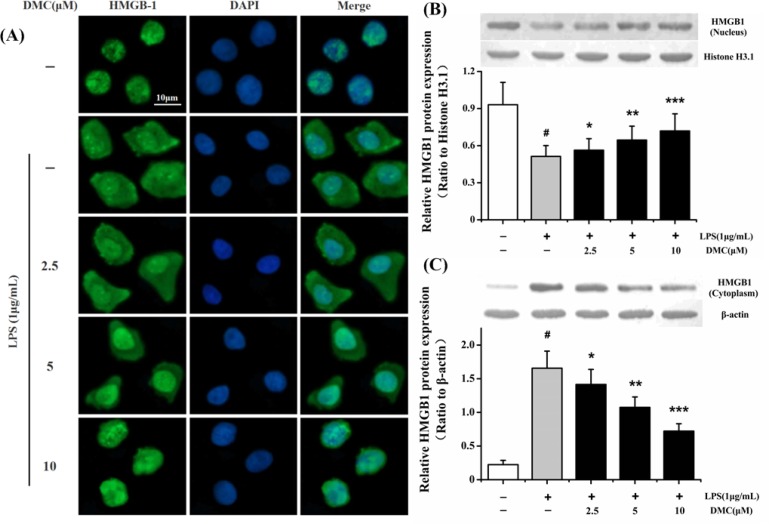
Fig. 4.
Inhibitory effect of DMC on the translocation of HMGB1 from nucleus to cytoplasm in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. The cells were pretreated with DMC for 2 h before LPS (1 μg/mL) treatment for 24 h. (A) HMGB1 nucleo-cytoplasmic translocation was assayed by laser scanning confocal microscopy. HMGB1 was mainly localized in nucleus of control group (first row). HMGB1 was distributed in both nuclear and cytoplasmic of LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells (second row). Pretreatment with DMC markedly inhibited LPS stimulated intracellular HMGB1 movement (third to fifth rows). Nucleus (blue, DAPI staining), HMGB1 (green). Bar: 10 μm. The nuclear and cytoplasmic HMGB1 proteins were measured via Western blot technique. (B) Histone H3.1 protein acted as loading control of nuclear HMGB1 protein. (C) β-actin protein acted as loading control of cytoplasmic HMGB1 protein. The bar graph showing semi-quantitative densitometric analysis summarizes the fold change of HMGB1 expression in each group. Each value represents the mean ± SD of triplicate experiments. #p<0.001 as compared with control group. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 as compared with LPS-induced group only.