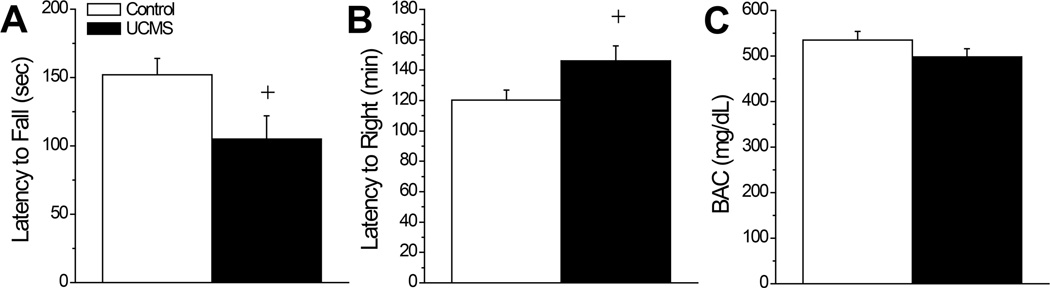
Figure 5.
Summary of the effects of our unpredictable chronic mild stress (UCMS) procedures upon alcohol intoxication and sedation. (A) When assessed on a fixed speed rotarod, UCMS mice (n=10) exhibited a shorter latency to fall when injected with 3 g/kg alcohol, compared to mice subjected to our control procedures (Control; n=9). (B) When injected with 5 g/kg, UCMS mice exhibited a longer latency to right in a regain of righting reflex study than did Controls. (C) The group differences in the sedative properties of 5 g/kg alcohol were not obviously related to an effect of UCMS upon BACs determined at 180 min post-injection (n=9/group). +p<0.05 vs. Control (t-tests).