Locally dynamic micrometer-scale domains based on spectrin and ankyrin-G determine membrane identity by preventing endocytosis.
Keywords: ankyrin-G, spectrin, palmitoylation, epithelial lateral membrane, clathrin, endocytosis, plasma membrane, microdomain
Abstract
Current physical models for plasma membranes emphasize dynamic 10- to 300-nm compartments at thermodynamic equilibrium but subject to thermal fluctuations. However, epithelial lateral membranes contain micrometer-sized domains defined by an underlying membrane skeleton composed of spectrin and its partner ankyrin-G. We demonstrate that these spectrin/ankyrin-G domains exhibit local microtubule-dependent movement on a time scale of minutes and encounter most of the lateral membranes within an hour. Spectrin/ankyrin-G domains exclude clathrin and clathrin-dependent cargo, and inhibit both receptor-mediated and bulk endocytosis. Moreover, inhibition of endocytosis fully restores lateral membrane height in spectrin- or ankyrin-G–depleted cells. These findings support a non-equilibrium cellular-scale model for epithelial lateral membranes, where spectrin/ankyrin-G domains actively patrol the plasma membrane, analogous to “window washers,” and promote columnar morphology by blocking membrane uptake.
Plasma membranes of metazoan cells provide the interface between cells and their tissues, where they mediate molecular transport, cell-cell contact, and signaling, and overall play critical roles in physiology. Current physical models for plasma membranes extend only to 200 to 300 nm, with the exception of red blood cells (RBCs) and axons whose membranes are uniformly coated with a mechanically resilient spectrin-based network (1–4). All of these models include dynamic behavior of membrane-spanning proteins and lipids that engage in thermal fluctuations, leading to random diffusion and transient associations within a fluid phospholipid bilayer. Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cell lateral membranes contain randomly spaced micrometer-sized domains highly enriched in the peripherally associated protein βII-spectrin and its partner, ankyrin-G (5, 6). These βII-spectrin/ankyrin-G domains cover less than half of the membrane area but are required for normal membrane height (5). As newly described membrane compartments, the physiological relevance of spectrin/ankyrin-G domains and how they promote lateral membrane formation are not known.
To determine whether ankyrin-G associates with membrane microdomains in tissues and cell culture, we compared native ankyrin-G in formaldehyde-fixed MDCK cells (Fig. 1A) and in paraffin sections of formaldehyde-fixed mouse kidney collecting ducts using deconvolution and three-dimensional (3D) restoration after confocal imaging with a high-resolution objective (fig. S1). Ankyrin-G labeling is markedly similar in MDCK cells and in kidney collecting ducts, where in both cases it is patterned into irregularly shaped domains 0.5 to 2 μm2 in area, which are confined to lateral membranes and cover about half of the membrane area.
Fig. 1. Ankyrin-G/βII-spectrin microdomains sample the entire lateral membrane through microtubule-dependent localized movement.
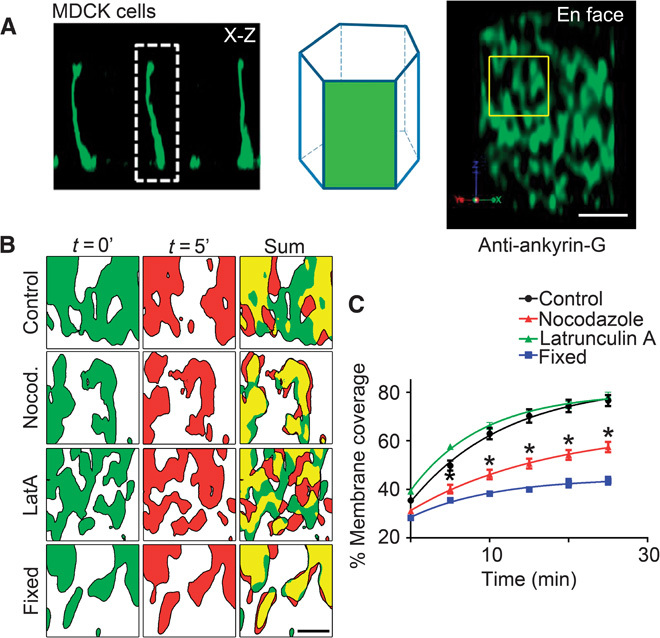
(A) Schematic depicting the en face visualization of the columnar epithelial cell lateral membrane. Representative deconvolved en face (right) image from MDCK cells stained with antibodies against endogenous ankyrin-G. Scale bar, 2.5 μm. Region of interest depicts size of area analyzed in (B). (B) Representative deconvolved en face confocal images of live MDCK cells transfected with ankyrin-G–GFP shown at time 0 (green) or 5 min (red) for control cells (top) or cells treated for 3 hours with nocodazole (Nocod.) (100 ng/ml) (second row) or 1 μM latrunculin A (LatA) (third row). Cells fixed with paraformaldehyde (bottom) were used as an imaging control. Summed coverage at 0 and 5 min shown on the right. Scale bar, 1 μm. (C) Quantification of percent lateral membrane coverage from cells in (B). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey post hoc test; *P < 0.05 compared to control, n = 4 to 9 cells per condition.
To determine spectrin/ankyrin-G domain lifetime and mobility, we imaged ankyrin-G–GFP (green fluorescent protein) in live MDCK cells. Ankyrin-G–GFP–labeled microdomains exhibited striking dynamic behavior on a local scale. When imaged at 5-min intervals, domains moved locally within the plane of the membrane, changed shape, and fused with each other (Fig. 1B and movie S1). Local gaps in ankyrin-G coverage are often filled and created within 5 min (Fig. 1B). The movement of ankyrin-G–GFP–labeled microdomains is sufficient to cover ~80% of the lateral membrane within 25 min (Fig. 1C). The movement was abolished by prefixing cells with paraformaldehyde and thus was not due to instrumental drift (Fig. 1C and movie S2). Similar movement was detected with βII-spectrin–GFP domains (movie S3).
Next, we asked if microdomain dynamics on the lateral membrane depended on either actin or microtubules. Pretreatment of ankyrin-G–GFP cells for 3 hours with the actin depolymerizing agent latrunculin A had no effect on membrane coverage by ankyrin-G (Fig. 1C and movie S4), despite efficient depolymerization of actin (fig. S2). In contrast, depolymerization of microtubules for 3 hours with nocodazole caused a substantial reduction in dynamics of ankyrin-G–labeled domains and reduced membrane coverage (Fig. 1C and movie S5). Stabilizing microtubules or actin with taxol or jasplakinolide, respectively, had no effect on microdomain movement or membrane coverage (fig. S3). The fact that microdomain dynamics occur independent of polymerization/depolymerization of microtubule plus ends suggests the possibility that these dynamics could be motor-driven. Another possibility is that the ankyrin/spectrin microdomains are disassembling and reassembling in a microtubule-dependent manner, perhaps through depalmitoylation or dephosphorylation of residues critical for ankyrin-G and βII-spectrin membrane association (5). In either case, these results demonstrate a requirement for microtubules in the dynamics of ankyrin-G–labeled microdomains within the plane of the lateral membrane.
MDCK cells contain a population of noncentrosomal microtubules running along the lateral membrane (7). These lateral membrane–associated microtubules colocalize with a subset of ankyrin-G–labeled microdomains at discrete puncta (fig. S4A). Depolymerization of microtubules with nocodazole also caused a marked loss of the lateral membrane from 8 to ~3.7 μm (fig. S4, B and C). Thus, depolymerization of microtubules, which reduced coverage of the lateral membrane by ankyrin-G–labeled domains (Fig. 1C), also reduced lateral membrane height.
Currently known configurations of spectrin as a polygonal network in erythrocyte membranes (8) or as a cylindrical lattice in axons (2) would prevent assembly of clathrin pits based on dimensions of these molecules (see schematic below). As an initial test of the idea that spectrin/ankyrin-G domains would exclude clathrin coats, we determined the spatial relationship between ankyrin-G and either clathrin heavy chain or clathrin cargo receptors (Fig. 2). As a positive control, ankyrin-G colocalized with wild-type βII-spectrin, but not Y1874A mutant βII-spectrin lacking ankyrin-binding activity, when these polypeptides were expressed in βII-spectrin–depleted cells (5) (Fig. 2). Although ankyrin-G and clathrin heavy chain were both localized to microdomains, these domains exhibited almost no colocalization on the lateral membrane (Pearson coefficient, 0.1; Fig. 2). Furthermore, two known clathrin cargoes, transferrin receptor (TfR) and the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR), were also present in microdomains that exhibited minimal colocalization with ankyrin-G [Pearson coefficients, 0.2 (TfR) and 0.1 (LDLR); Fig. 2]. These results demonstrate that spectrin/ankyrin-G domains exclude clathrin and its cargoes.
Fig. 2. Ankyrin-G co-patterns with βII-spectrin in lateral membrane microdomains that are distinct from clathrin and its cargoes.

(A) Representative deconvolved en face confocal images of MDCK cell lateral membranes stained for endogenous ankyrin-G (AnkG) (green). βII-spectrin–GFP, βII-spectrin Y1874A–GFP, clathrin heavy chain (CHC), LDLR (LDLR-GFP), and transferrin receptor–yellow fluorescent protein (TfR-YFP) are shown in red. Positive displacement from the mean colocalization is shown in yellow. Merged image is on the right. Scale bars, 2.5 μm. (B) Quantification of Pearson coefficient of colocalization from (A).
The gaps between spectrin/ankyrin-G domains are often filled within 5 min (Fig. 1, B and C), which is similar to the time required to form clathrin-coated pits and plaques (9, 10). The striking segregation of spectrin/ankyrin-G domains and clathrin in fixed samples combined with movement of microdomains with similar kinetics to endocytosis suggested the hypothesis that spectrin/ankyrin-G domains would globally inhibit clathrin-mediated endocytosis over the entire lateral membrane. Therefore, we developed a system for inducible expression of the truncated, soluble ankyrin-binding domain from βII-spectrin, which competes for native ankyrin-G–β-spectrin interactions (11). To acutely express this construct within one cell division cycle, we generated a stable cell line expressing a fusion protein of the ankyrin-binding domain of βII-spectrin with an FKBP-based destabilization domain (Fig. 3A) that confers instability and continuous degradation of the fusion protein in the absence of the Shield-1 ligand (12). The addition of Shield-1 resulted in a rapid time- and dose-dependent increase in expression of the DsRed-tagged dominant-negative polypeptide (Fig. 3, B and C). We measured fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)–transferrin uptake by incubating MDCK cells grown on Transwell filters for 60 min with FITC-labeled transferrin in the basolateral medium. MDCK cells in the absence of Shield-1 displayed modest transferrin uptake from the lateral membrane (Fig. 3, C and D). The expression of the ankyrin-binding domain by the addition of Shield-1 for 24 hours increased transferrin endocytosis from the lateral membrane by >50% (Fig. 3, C and D). The increase in transferrin endocytosis was specifically caused by the disruption of the ankyrin-G/βII-spectrin interaction because activity was abolished by a Y1874A mutation of the ankyrin-binding domain that eliminates binding to ankyrin (13, 14) (Fig. 3, C and D). These results demonstrate that perturbing interaction between ankyrin-G and βII-spectrin promotes endocytosis of transferrin from the lateral membrane.
Fig. 3. Disruption of ankyrin-G/βII-spectrin interaction or silencing of ankyrin-G increases bulk endocytosis from the epithelial lateral membrane.
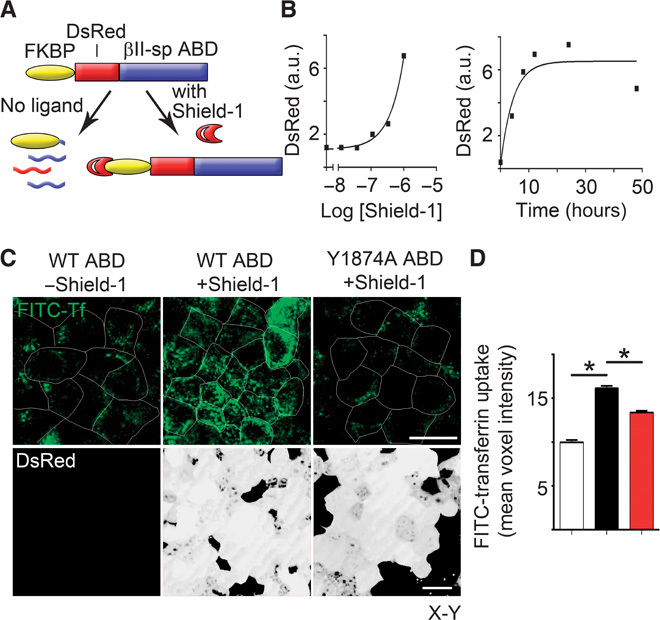
(A) Schematic for tunable expression of a dominant-negative fragment consisting of the ankyrin-binding domain (ABD) of βII-spectrin that disrupts the interaction between βII-spectrin and ankyrin-G. (B) (Left) Dose-response curve for increase in DsRed expression as determined by Western blot in response to 24-hour addition of indicated doses of Shield-1. (Right) Time course of Western blot levels of FKBP-DsRed-ABD in cells treated with 1 μM Shield-1. a.u., arbitrary units. (C) Representative X-Y confocal images of FITC-transferrin uptake (top, green) from the basolateral membrane of MDCK cells in the absence (left) or presence (middle) of the ankyrin-binding domain dominant negative, or in the presence of a control that lacks ankyrin-binding activity (right). DsRed-tagged dominant-negative expression is shown on the bottom (white). Scale bars, 20 μm. Cell borders are shown in white. WT, wild type. (D) Quantification of FITC-transferrin uptake from (A) in the absence (white) or presence (black) of the ankyrin-binding domain dominant negative, or in the presence of a control that lacks ankyrin-binding activity (red). One-way ANOVA, Tukey post hoc test; *P < 0.05, n = 86 to 120.
Next, we examined whether the increase in endocytosis from the lateral membrane was limited to receptors or represented bulk behavior of the entire membrane compartment. To address this question, we used an amphipathic plasma membrane marker (a proprietary compound termed CellMask) to label the plasma membrane and evaluated membrane internalization in MDCK cell lines 45 min after adding CellMask. Cells expressing control short hairpin RNA (shRNA) against luciferase exhibited only a sparse population of vesicles near the lateral membrane (Fig. 4A). In contrast, ankyrin-G–depleted cells (>80% depleted; Fig. 5C) exhibited a marked increase in vesicles near the lateral membrane (Fig. 4A). The increase in vesicles from the lateral membrane was reversed by treatment with dynasore, which inhibits both clathrin-dependent and some forms of clathrin-independent endocytosis (15) (Fig. 4A). Similar results were obtained with cells expressing shRNA against βII-spectrin (Fig. 4B) exhibiting >90% loss of βII-spectrin (5). Thus, loss of ankyrin-G or βII-spectrin causes a robust increase in dynasore-sensitive endocytosis of bulk lipids from the lateral membrane of columnar epithelial cells.
Fig. 4. Depletion of ankyrin-G or βII-spectrin causes a marked increase in lipid uptake from the lateral membrane, which is reversed by dynasore treatment.

(A) Representative X-Y images of MDCK cells demonstrating internalization of CellMask (red) in the presence of luciferase (Luc) shRNA (left), ankyrin-G shRNA (middle), or ankyrin-G shRNA plus 80 μM dynasore (right). Arrowheads mark internalized vesicles. Higher magnification of yellow region of interest (ROI) is shown below. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) Representative X-Y images of MDCK cells demonstrating internalization of CellMask (red) in the presence of luciferase shRNA (left), βII-spectrin shRNA (middle), or βII-spectrin plus 80 μM dynasore (right). Arrowheads mark internalized vesicles. Higher magnification of yellow region of interest is shown below. Scale bar, 10 μm.
Fig. 5. Silencing of clathrin heavy chain in ankyrin-G–depleted cells restores lateral membrane height.
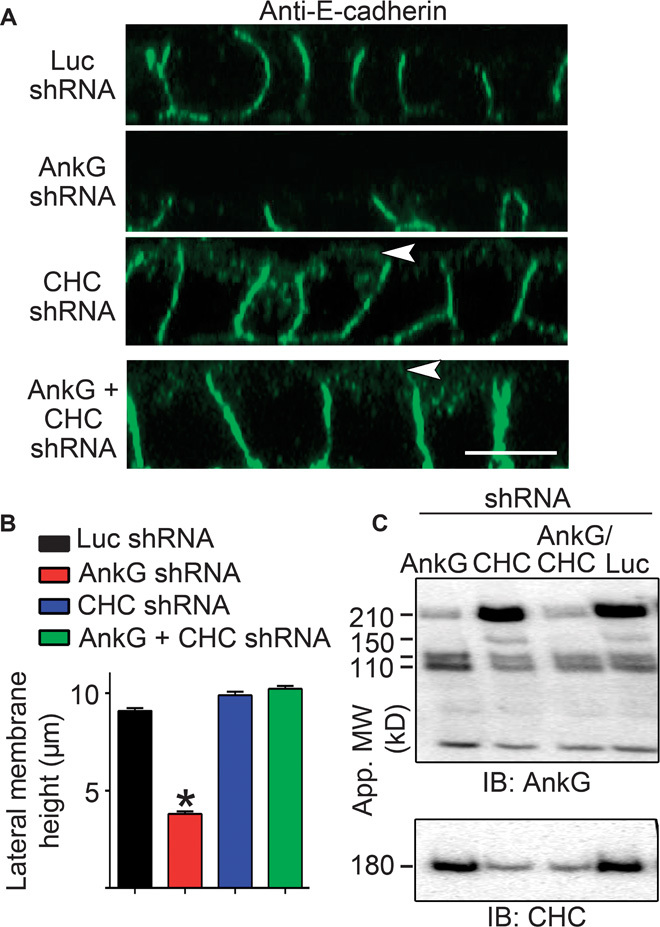
(A) Representative X-Z projections of confocal stacks of MDCK cells expressing shRNA to luciferase (Luc, top), ankyrin-G (second row), clathrin heavy chain (CHC, third row), or both ankyrin-G and CHC (bottom) stained for E-cadherin (green). Arrowheads mark apical mislocalization of E-cadherin. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) Quantification of lateral membrane height from (A). One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc test; *P < 0.05 compared to Luc shRNA. n = 60 to 65. (C) Western blot of MDCK cells stably expressing inducible shRNA against ankyrin-G, CHC, both ankyrin-G and CHC, or luciferase as a control. Cells were preinduced with doxycycline for 24 hours, trypsinized, and replated for an additional 24 hours in medium containing doxycycline. Ankyrin-G shown on top, with loss of the 210- and 150-kD isoforms. The 120/110-kD isoforms, which are not targeted by this shRNA sequence, are spared. CHC levels are shown on bottom.
We next explored the hypothesis that dynamic spectrin/ankyrin-G microdomains promote lateral membrane height by opposing endocytosis. A prediction of this mechanism is that inhibition of endocytosis would restore lateral membrane height in ankyrin-G– or βII-spectrin–deficient cells. To directly test this idea, we examined the effects of clathrin heavy chain knockdown on cell height in ankyrin-G–depleted cells (Fig. 5, A to C). Silencing of ankyrin-G alone, which results in more than 80% loss of the 210-kD ankyrin-G polypeptide (Fig. 5C), caused a reduction in lateral membrane height from 9 to 10 μm to less than 4 μm (Fig. 5, A and B) (5, 16, 17). In contrast, silencing of clathrin heavy chain expression with 80 to 90% loss of the 180-kD polypeptide (Fig. 5C) had no effect on lateral membrane height but did cause apical mislocalization of E-cadherin, as previously reported (16, 18). However, shRNA-mediated silencing of both ankyrin-G and clathrin heavy chain fully restored lateral membrane height to ~9 μm, indistinguishable from wild-type cell heights (Fig. 5, A to C). Moreover, 24-hour treatment with 80 μM dynasore completely restored the lateral membrane of ankyrin-G–depleted cells to levels indistinguishable from wild-type cells (Fig. 6, A and B). Furthermore, loss of lateral membrane through βII-spectrin silencing was also rescued by dynasore treatment (Fig. 6, A and B). Together, these results demonstrate that loss of lateral membrane height due to deficiency of either ankyrin-G or βII-spectrin can be fully reversed by inhibiting endocytosis. In genetic terms, these results demonstrate that clathrin and ankyrin-G/βII-spectrin are epistatic to each other in the lateral membrane assembly pathway and that loss of clathrin functions to suppress the ankyrin-G/βII-spectrin phenotype.
Fig. 6. Loss of lateral membrane caused by silencing of ankyrin-G or βII-spectrin is reversed by inhibiting endocytosis.
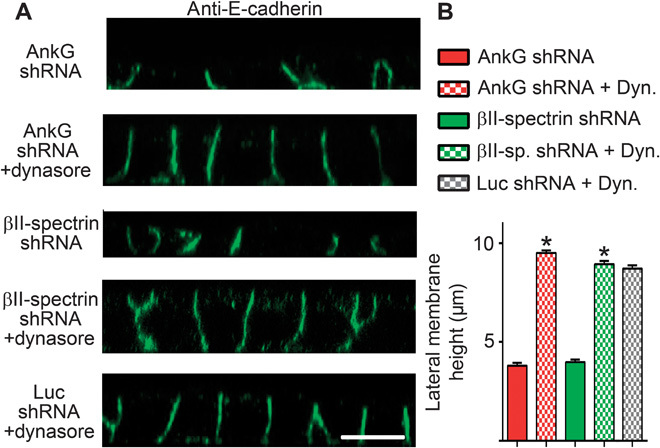
(A) Representative X-Z projections of confocal stacks of MDCK cells expressing shRNA to ankyrin-G or βII-spectrin, with or without treatment with the endocytosis inhibitor dynasore. Cells stained for E-cadherin (green). Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) Quantification of lateral membrane height from (A). One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc test; *P < 0.05 compared to without dynasore. n = 50 to 75.
In summary, we present a new physical model for epithelial lateral membranes, where dynamic micrometer-scale compartments composed of spectrin and ankyrin-G actively patrol the membrane through a microtubule-dependent mechanism, analogous to “window washers,” and prevent both receptor-mediated and bulk endocytosis. Thus, lateral membrane spectrin is not configured as a uniform polymeric structure covering the entire membrane, as in erythrocytes and axons, but rather is confined to microdomains, which are in homeostatic equilibrium with endocytic processes (Fig. 7, A and B). Our model is based on the known density of erythrocyte ankyrin/spectrin networks visualized in membranes isolated under nonnative conditions of low ionic strength. The actual density of spectrin is likely much higher in unextracted erythrocytes based on platinum replica electron microscopy (19). It will be challenging but important to determine the configuration of epithelial lateral membrane ankyrin/spectrin networks. Giant ankyrin-G is configured together with βII-spectrin in microdomains in the somatodendritic plasma membranes of hippocampal neurons and stabilizes GABAergic synapses through opposing endocytosis (20). Thus, the concept of plasma membrane domains as a dynamic balance between stabilization through spectrin/ankyrin and endocytosis applies to both neurons and epithelial cells.
Fig. 7. Model of lateral membrane domain organization.
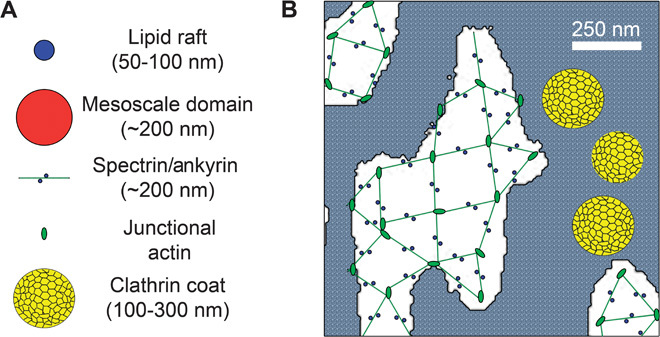
(A) Representations of relative sizes of lipid rafts, mesoscale domains, the spectrin/ankyrin complex, junctional actin, and a clathrin coat. Note: size of junctional actin based on size of erythrocyte junctional actin. (B) Schematic representation of an ankyrin-G/spectrin lattice overlaid onto an image of spectrin/ankyrin-G lateral membrane domains (white areas). Note that where clathrin pits are in close proximity, they will appear as a fused patch at the 250-nm resolution of the light microscope. The remaining plasma membrane is indicated by gray stipple. Scale bar, 250 nm. The extended configuration of spectrin tetramers is based on the negative-stained images or erythrocytes obtained in low ionic strength (8). However, platinum replica imaging of native erythrocyte membranes indicates that spectrin exists in a much more compressed configuration with correspondingly smaller gaps (19).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plasmids
Wild-type 190-kD ankyrin-G–GFP, C70A ankyrin-G–GFP, βII-spectrin–GFP and Y1874A βII-spectrin–GFP, and E-cadherin–GFP were previously described (5, 6, 21, 22). Ankyrin-G–mCherry was generated by replacing the GFP from ankyrin-G–GFP with mCherry using standard cloning techniques. LDLR-GFP was a gift from T. Jensen (Aarhus University, Denmark). TfR-YFP was a gift from A. M. J. VanDongen (Duke University). FKBP (L106P) plasmid (12) was a gift from T. Wandless (Stanford University). A cassette containing a c-myc epitope, DsRed, and the dominant-negative ankyrin-binding fragment of βII-spectrin [repeats 14 to 16 (11)] was inserted downstream of the FKBP destabilization domain using standard cloning techniques. The resulting FKBP–myc–DsRed–βII-spectrin ABD cassette was inserted into pLenti6 V5-DEST (Life Technologies) using Gateway cloning. The pLKO Tet-On 2A-BFP based on pLKO Tet-On (23, 24) was previously described (5). Lentiviral packaging plasmids (psPAX2 and pMD2.G) were from Addgene.
Reagents and antibodies
Mouse anti–E-cadherin (1:250; BD Biosciences), mouse CHC (1:250 immunofluorescence, 1:2000 Western blot; BD Biosciences), mouse anti–glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) (1:5000; Abcam), chicken anti-GFP (1:500; Abcam), rabbit anti–ankyrin-G C-terminal ankyrin-G [1:500 immunofluorescence, 1:5000 Western blot (21)], and rabbit anti–βII-spectrin antibodies [1:500 immunofluorescence, 1:5000 Western blot (5)] and secondary antibodies conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488, 568, or 647 (1:250) were used. CellMask, latrunculin A, taxol, and jasplakinolide were from Life Technologies. FITC-transferrin was from Jackson ImmunoResearch. Shield-1 compound was a gift from T. Wandless (Stanford University). Nocodazole, doxycycline, and dynasore were from Sigma-Aldrich.
Tissue preparation and immunohistochemistry
Tissue preparation was performed as previously described (16). Briefly, neonatal mouse pups were sacrificed by decapitation. Kidneys were removed and fixed overnight in 4% paraformaldehyde followed by an automated standard [phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) wash followed by dehydrations through 70, 95, and 100% ethanol with final incubations in xylene and hot paraffin under vacuum]. Final paraffin embedding was completed the following day. Paraffin sections were cut at 7 μm using a Leica RM2155 microtome, deparaffinized, and rehydrated through a series of ethanol washes (100 to 70%). Sections were blocked using the Vector MOM kit (Vector Laboratories) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Slides were incubated overnight at 4°C with anti–ankyrin-G antibodies (1:500) diluted in blocking buffer (3% fish oil, 10% horse serum, 0.1% Tween in PBS). After extensive PBS washing, slides were incubated in blocking buffer with the appropriate secondary antibodies for 1 hour at room temperature, washed, and mounted with ProLong Gold Antifade reagent (Life Technologies).
Inducible shRNA cell lines
Inducible shRNA cell lines were generated as previously described (5). Modified pLKO 2A-BFP was packaged into lentiviral particles using psPAX2 and pMD2.G in HEK293T/17 cells. Viral particles were harvested after 48 hours. On the day of infection, 0.5 × 106 MDCK cells were mixed with virus and polybrene (8 μg/ml) and plated in six-well dishes. Sixteen hours later, the cells were extensively washed to remove viral particles and then grown in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). The next day, cells were trypsinized and sorted for the brightest TagBFP population (~1%), which can be maintained as a stable cell line. Hairpins used to target canine ankyrin-G, clathrin heavy chain, βII-spectrin, DHHC5/8, and luciferase were previously described (5, 16). Ankyrin-G/CHC double shRNA cells were generated using pLKO Tet-On 2A-mCherry ankyrin-G shRNA (16) and pLKO Tet-On 2A-TagBFP CHC shRNA.
Transfection and immunofluorescence
MDCKII cells were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection and maintained in a humidified environment at 37°C with 5% CO2. Cells were cultured in DMEM (Invitrogen #11995) with 10% FBS, penicillin (100 U/ml), and streptomycin (100 U/ml). For transfection, 1.5 × 105 MDCK cells were plated in normal growth medium in the center of a 14-mm well MatTek glass-bottomed dish and allowed 4 hours to adhere. Plasmids (100 to 300 ng) were transfected using Lipofectamine 2000 (Life Technologies) according to the manufacturer’s protocol and added directly to the center well of the MatTek dish. After 12 to 16 hours, cells were fed with 2 ml of growth medium and allowed 24 to 48 hours for expression.
For immunofluorescence, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min at room temperature, permeabilized for 10 min with 0.1% Triton X-100, and blocked in blocking buffer (5% bovine serum albumin, 0.2% Tween 20 PBS). Samples were incubated overnight at 4°C with primary antibodies diluted in blocking buffer. After extensive washing with PBS, samples were incubated for 1 hour with secondary antibodies diluted in blocking buffer, extensively washed with PBS, and mounted with ProLong Gold Antifade reagent. For endogenous βII-spectrin staining, samples were prepared as described above, except fixation was performed with 1% paraformaldehyde for 1 hour at 4°C. For microtubule staining, samples were extracted in microtubule-stabilizing buffer [80 mM Pipes (pH 6.8), 1 mM MgCl2, 5 mM EGTA] with 0.5% Triton X-100 for 30 s. Glutaraldehyde was added to 0.5% final concentration for 10 min at room temperature. Samples were quenched with fresh 0.1% sodium borohydride, rinsed well with PBS, and immunostained as described above.
Lateral membrane rescue
For pharmacological rescue of lateral membrane height, doxycycline-inducible shRNA 107 MDCKII cells were preinduced for 24 hours with doxycycline (5 μg/ml). Cells were trypsinized and plated at confluence (5 × 105 cells in the center of a 14-mm MatTek dish) in growth medium and allowed 4 hours to adhere. Cells were then fed with 2 ml of growth medium in the presence or absence of 80 μM dynasore, an inhibitor of endocytosis. For plasmid-based rescue, after preinduction with doxycycline, 1.5 × 105 cells were plated in a MatTek dish. After 8 hours, cells were washed and transfected with 150 ng of rescue plasmid as described above. After 24 hours, the cells were fixed and prepared for immunostaining.
For microtubule depolymerization experiments, ankyrin-G shRNA stable MDCK cells were preinduced with doxycycline (5 mg/ml) for 24 hours to silence endogenous ankyrin-G. Preinduced cells (5 × 105) were plated in the 14-mm insert of the MatTek dishes in the presence of doxycycline (5 mg/ml). Six to 8 hours later, the plates were gently washed with PBS to remove nonattached cells, and incubated with complete medium with doxycycline (5 mg/ml), nocodazole (100 ng/ml), and 80 μM dynasore [or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as a control] for 24 hours. Cells were then fixed and immunostained for endogenous E-cadherin to visualize lateral membranes.
CellMask uptake
Ankyrin-G or luciferase shRNA stable MDCK cells were preinduced with doxycycline (4 μg/ml) for 24 hours to silence indicated genes. Preinduced cells (5 × 105) were plated in the 14-mm insert of the MatTek dishes in the presence of doxycycline (5 mg/ml). Six to 8 hours later, the plates were gently washed with PBS to remove nonattached cells, and incubated with complete medium with doxycycline (5 mg/ml) and 80 μM dynasore (or DMSO as a control). Twenty-four hours later, cells were washed with prewarmed PBS three times and incubated at 37°C, 5% CO2 with CellMask Orange plasma membrane stain at 1× concentration for 45 min. Cells were washed with prewarmed PBS once and live-imaged at 37°C, 5% CO2 on the Zeiss 780 LSM confocal microscope.
Transferrin uptake
For transferrin uptake experiments, wild-type or Y1874A ABD stable cell lines were generated by lentiviral infection and cell sorting using DsRed expression to achieve a highly expressing population. Sorted cells were plated at confluence on Transwell filters (5 × 105 cells on 6.5-mm Transwell with 0.4-μm pores). After 4 hours, cells were washed to remove nonadherent cells, and medium was replaced with normal growth medium plus 1 μM Shield-1 (or DMSO as a control). After 24 hours, cells were incubated for 1 hour in serum-free DMEM and then with FITC-transferrin (100 mg/ml) in normal growth medium on the basolateral side for 60 min at 37°C and 5% CO2. Cells were washed with cold DMEM on ice three times and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min. Filters were excised and mounted with ProLong Gold.
Microscopy
Imaging for fixed samples was performed at room temperature using an inverted confocal microscope (LSM780; Carl Zeiss) with a 63×, numerical aperture (NA) 1.40, or 100×, NA 1.45 oil objective lenses or a Nikon A1R with a 60×, NA 1.40 oil objective. XZ planes were reconstructed from Z-stacks with optical sections of 250 nm using the ZEN 2012 software. For live imaging, the incubation chamber was maintained at 37°C, 5% CO2, and cells were maintained in physiological saline solution (141 mM NaCl, 5.6 mM KCl, 2.2 mM CaCl2, 0.5 mM MgCl2, 5.6 mM glucose, 15 mM Hepes, pH 7.4). For 3D deconvolution microscopy, images were collected at room temperature using the 100×, NA 1.45, objective lens with optical sections of 250 nm and subjected to 3D deconvolution in Volocity 3D Image Analysis Software (PerkinElmer) with a measured point spread function generated with 100-nm beads (axial spacing in Z, 0.25 μm; lateral spacing in XY, 0.0277 μm; medium reference index, 1.52; NA, 1.45; detector pinhole size, 1 Airy unit). 3D representations of deconvolved lateral membranes were rotated en face in Volocity software to display protein organization within the plane of the membrane.
Microdomain movement
Microdomain movement within the plane of the lateral membrane of ankyrin-G–GFP stable MDCK cells was monitored by capturing Z-stacks at a 250-nm axial spacing every 5 min for 30 min. Samples were deconvolved and processed as described in Microscopy. Resulting time series images were imported into the National Institutes of Health (NIH) ImageJ software, converted to 8-bit images, and thresholded to equivalent levels. Coverage of the lateral membrane was calculated by summing the binary images at each time point. For pharmacology experiments, cells were imaged at 37°C and 5% CO2 first before the addition of drugs and then again 3 hours after the addition of drugs [1 μM latrunculin A or nocodazole (100 ng/ml)] in physiological saline. For fixed control, cells were prefixed for 30 min in 4% paraformaldehyde and imaged as described above. For microdomain movement of ankyrin-G and E-cadherin, MDCK cells were transfected with 300 ng each of ankyrin-G–mCherry and E-cadherin–GFP as described above. Cells were imaged 48 hours later.
Statistical and data analysis
Measurements were taken using the Zeiss Zen or NIH ImageJ software and repeated for at least three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed with Prism software (GraphPad). Data shown are means ± SEM. One-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test was used to compare three or more groups.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank T. Wandless (Stanford University) for providing the FKBP plasmid and Shield-1 compound. Funding: Funding was provided by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. Author contributions: P.M.J., M.H., and V.B. designed the study. P.M.J. and M.H. acquired, analyzed, and interpreted data. P.M.J. and V.B. drafted the manuscript. M.H. provided critical revision of the manuscript. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Data and materials availability: All data is included in the paper.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary material for this article is available at http://advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/8/e1500301/DC1
Fig. S1. Ankyrin-G patterns into micrometer-scale domains in mouse kidney epithelial lateral membranes.
Fig. S2. Latrunculin A and nocodazole treatments effectively depolymerize the MDCK microtubule and actin cytoskeleton, respectively.
Fig. S3. Stabilization of microtubules or actin does not affect dynamics of ankyrin-G microdomains or lateral membrane coverage.
Fig. S4. Microtubules colocalize with ankyrin-G microdomains at discrete sites and are required for lateral membrane biogenesis.
Movie S1. Live imaging of ankyrin-G–GFP on the lateral membrane of control MDCK cells.
Movie S2. Live imaging of ankyrin-G–GFP on the lateral membrane of paraformaldehyde-fixed MDCK cells.
Movie S3. Live imaging of βII-spectrin–GFP on the lateral membrane of MDCK cells treated with latrunculin A.
Movie S4. Live imaging of ankyrin-G–GFP on the lateral membrane of MDCK cells treated with latrunculin A.
Movie S5. Live imaging of ankyrin-G–GFP on the lateral membrane of MDCK cells treated with nocodazole.
REFERENCES AND NOTES
- 1.Kusumi A., Fujiwara T. K., Morone N., Yoshida K. J., Chadda R., Xie M., Kasai R. S., Suzuki K. G., Membrane mechanisms for signal transduction: The coupling of the meso-scale raft domains to membrane-skeleton-induced compartments and dynamic protein complexes. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 23, 126–144 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Xu K., Zhong G., Zhuang X., Actin, spectrin, and associated proteins form a periodic cytoskeletal structure in axons. Science 339, 452–456 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fowler V. M., The human erythrocyte plasma membrane: A Rosetta Stone for decoding membrane–cytoskeleton structure. Curr. Top. Membr. 72, 39–88 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Saka S. K., Honigmann A., Eggeling C., Hell S. W., Lang T., Rizzoli S. O., Multi-protein assemblies underlie the mesoscale organization of the plasma membrane. Nat. Commun. 5, 4509 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.He M., Abdi K. M., Bennett V., Ankyrin-G palmitoylation and βII-spectrin binding to phosphoinositide lipids drive lateral membrane assembly. J. Cell Biol. 206, 273–288 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.He M., Jenkins P., Bennett V., Cysteine 70 of ankyrin-G is S-palmitoylated and is required for function of ankyrin-G in membrane domain assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 43995–44005 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bacallao R., Antony C., Dotti C., Karsenti E., Stelzer E. H., Simons K., The subcellular organization of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells during the formation of a polarized epithelium. J. Cell Biol. 109, 2817–2832 (1989). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Byers T. J., Branton D., Visualization of the protein associations in the erythrocyte membrane skeleton. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 6153–6157 (1985). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Saffarian S., Cocucci E., Kirchhausen T., Distinct dynamics of endocytic clathrin-coated pits and coated plaques. PLOS Biol. 7, e1000191 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Loerke D., Mettlen M., Yarar D., Jaqaman K., Jaqaman H., Danuser G., Schmid S. L., Cargo and dynamin regulate clathrin-coated pit maturation. PLOS Biol. 7, e57 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hu R. J., Moorthy S., Bennett V., Expression of functional domains of beta G-spectrin disrupts epithelial morphology in cultured cells. J. Cell Biol. 128, 1069–1080 (1995). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Banaszynski L. A., Chen L.-C., Maynard-Smith L. A., Ooi A. G., Wandless T. J., A rapid, reversible, and tunable method to regulate protein function in living cells using synthetic small molecules. Cell 126, 995–1004 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Davis L., Abdi K., Machius M., Brautigam C., Tomchick D. R., Bennett V., Michaely P., Localization and structure of the ankyrin-binding site on β2-spectrin. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 6982–6987 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ipsaro J. J., Mondragon A., Structural basis for spectrin recognition by ankyrin. Blood 115, 4093–4101 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Macia E., Ehrlich M., Massol R., Boucrot E., Brunner C., Kirchhausen T., Dynasore, a cell-permeable inhibitor of dynamin. Dev. Cell 10, 839–850 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jenkins P. M., Vasavda C., Hostettler J., Davis J. Q., Abdi K., Bennett V., E-cadherin polarity is determined by a multifunction motif mediating lateral membrane retention through ankyrin-G and apical-lateral transcytosis through clathrin. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 14018–14031 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kizhatil K., Bennett V., Lateral membrane biogenesis in human bronchial epithelial cells requires 190-kDa ankyrin-G. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 16706–16714 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Deborde S., Perret E., Gravotta D., Deora A., Salvarezza S., Schreiner R., Rodriguez-Boulan E., Clathrin is a key regulator of basolateral polarity. Nature 452, 719–723 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Harding C., Heuser J., Stahl P., Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and recycling of the transferrin receptor in rat reticulocytes. J. Cell Biol. 97, 329–339 (1983). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tseng W. C., Jenkins P. M., Tanaka M., Mooney R., Bennett V., Giant ankyrin-G stabilizes somatodendritic GABAergic synapses through opposing endocytosis of GABAA receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112, 1214–1219 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kizhatil K., Yoon W., Mohler P. J., Davis L. H., Hoffman J. A., Bennett V., Ankyrin-G and β2-spectrin collaborate in biogenesis of lateral membrane of human bronchial epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 2029–2037 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kizhatil K., Davis J. Q., Davis L., Hoffman J., Hogan B. L. M., Bennett V., Ankyrin-G is a molecular partner of E-cadherin in epithelial cells and early embryos. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 26552–26561 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wiederschain D., Susan W., Chen L., Loo A., Yang G., Huang A., Chen Y., Caponigro G., Yao Y.-., Lengauer C., Sellers W. R., Benson J. D., Single-vector inducible lentiviral RNAi system for oncology target validation. Cell Cycle 8, 498–504 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wee S., Wiederschain D., Maira S.-M., Loo A., Miller C., deBeaumont R., Stegmeier F., Yao Y.-M., Lengauer C., phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)-deficient cancers depend on PIK3CB. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 13057–13062 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material for this article is available at http://advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/8/e1500301/DC1
Fig. S1. Ankyrin-G patterns into micrometer-scale domains in mouse kidney epithelial lateral membranes.
Fig. S2. Latrunculin A and nocodazole treatments effectively depolymerize the MDCK microtubule and actin cytoskeleton, respectively.
Fig. S3. Stabilization of microtubules or actin does not affect dynamics of ankyrin-G microdomains or lateral membrane coverage.
Fig. S4. Microtubules colocalize with ankyrin-G microdomains at discrete sites and are required for lateral membrane biogenesis.
Movie S1. Live imaging of ankyrin-G–GFP on the lateral membrane of control MDCK cells.
Movie S2. Live imaging of ankyrin-G–GFP on the lateral membrane of paraformaldehyde-fixed MDCK cells.
Movie S3. Live imaging of βII-spectrin–GFP on the lateral membrane of MDCK cells treated with latrunculin A.
Movie S4. Live imaging of ankyrin-G–GFP on the lateral membrane of MDCK cells treated with latrunculin A.
Movie S5. Live imaging of ankyrin-G–GFP on the lateral membrane of MDCK cells treated with nocodazole.


