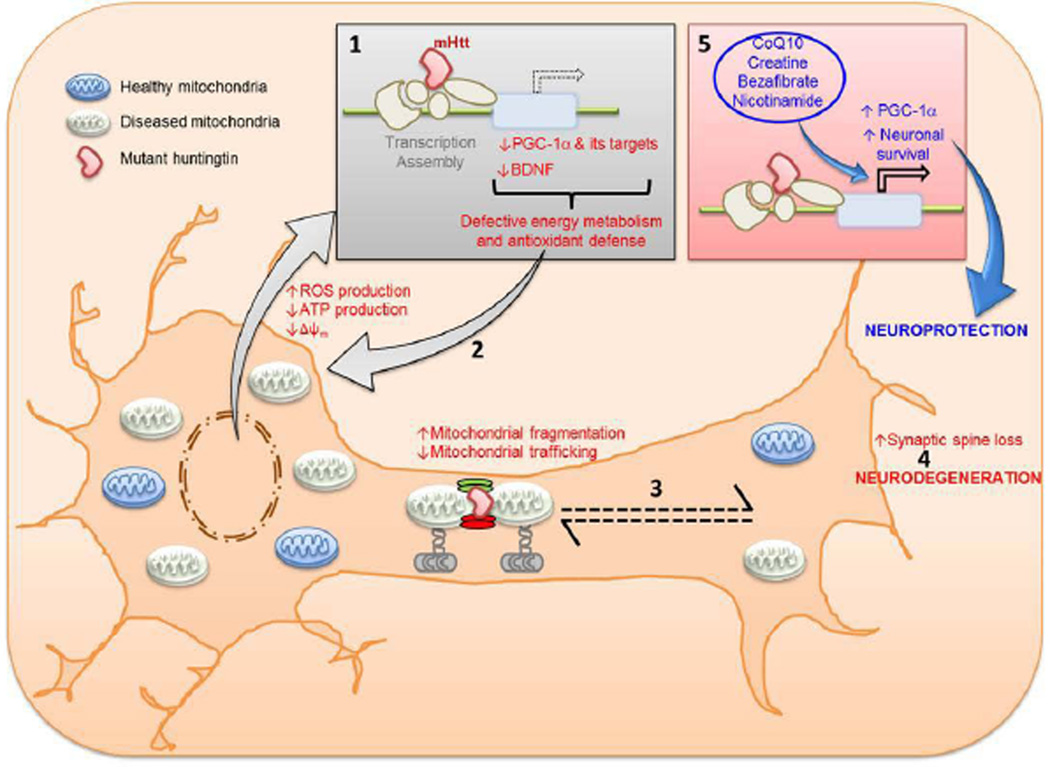
Figure 3.
Transcriptional interference of mutant huntingtin (mHtt) with PGC-1α produces defective energy metabolism and antioxidant defense (1) resulting in increased reactive oxygen species production, which in turn damage more mitochondria (2). Mutant huntingtin also interferes with mitochondrial fission-fusion process tipping the balance towards increased fission and interferes with vesicular transport (3). The net result of these impairments is low ATP at nerve terminals which culminates in neuronal death (4). Pharmacologic treatments with CoQ10, creatine, bezafibrate and nicotinamide increase PGC-1α and protect against neuronal death (5).