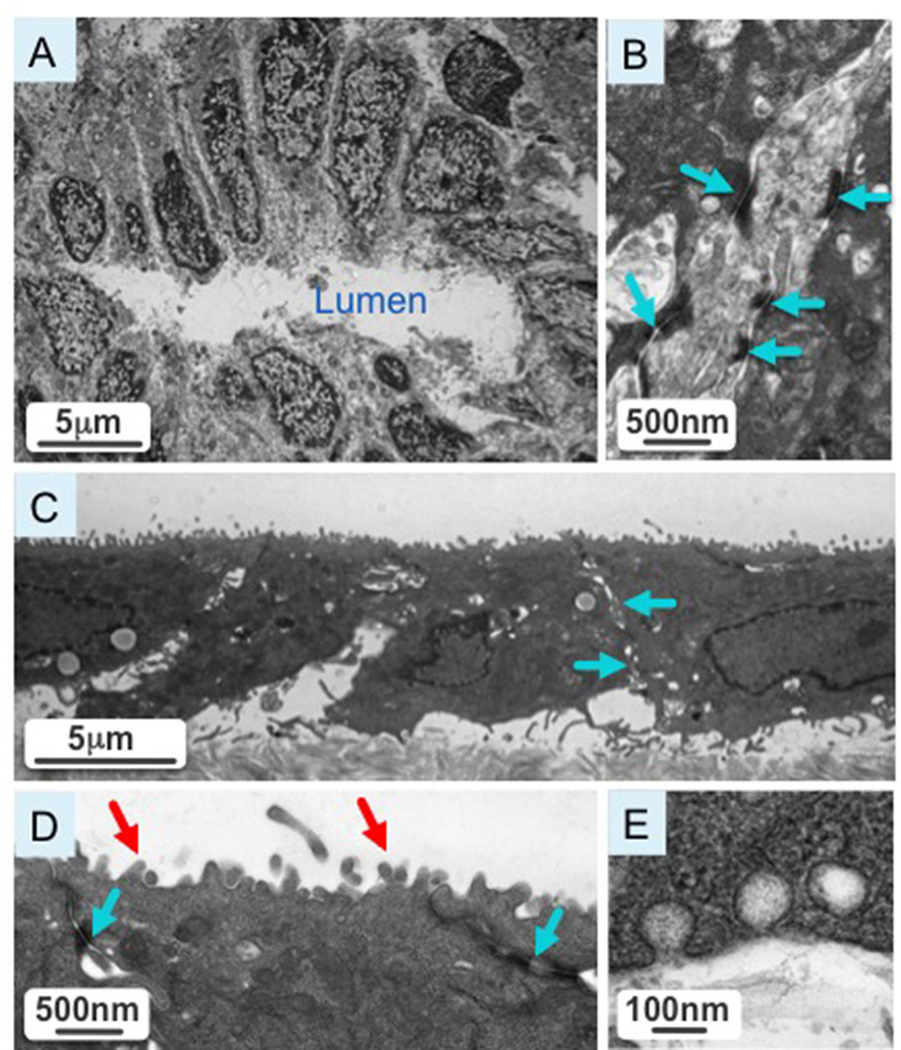
Figure 2.
[A] Cross-section of a normal extrahepatic bile duct with cholangiocytes polarized around the bile duct lumen. [B] A higher magnification image of the cross-section shows intact tight junction (blue arrows) characteristic of biliary epithelia. [C] A representative picture shows isolated extrahepatic cholangiocytes cultured on transwells. [D] A higher magnification image of cultured cholangiocytes reveals intact tight junctions (blue arrows) and an abundance of microvilli (red arrow) at the apical surface. [E] Cultured cholangiocytes have vesicular invaginations at the apical and basolateral poles, suggestive of active secretory and absorptive processes characteristic of bile duct epithelia.