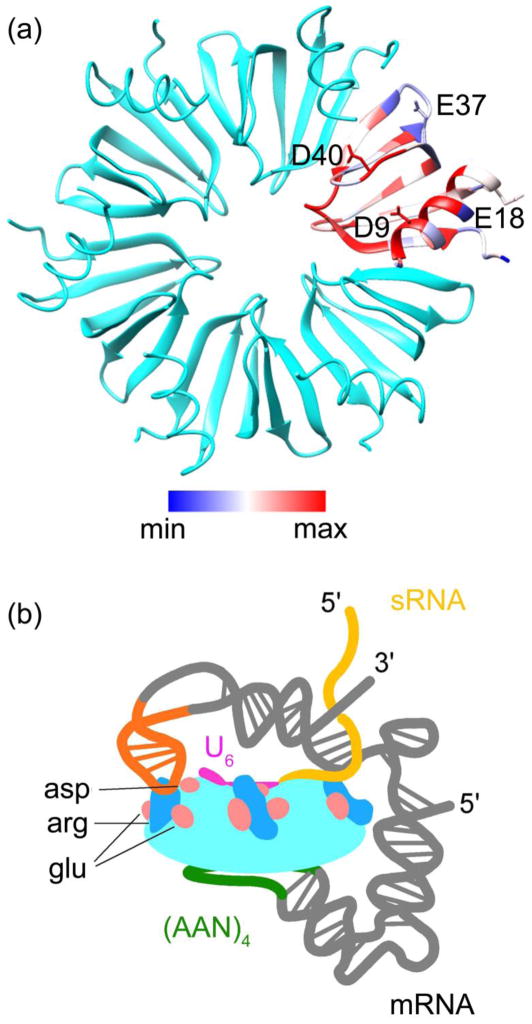
Fig. 1. Conserved acidic residues on the Hfq proximal surface.
(a) Conservation scores of 145 Hfq sequence clusters were rendered from blue (minimum) to magenta (maximum) on one subunit of the hexamer (chain A; 1HK9). Acidic residues (D9, E18, E37 and D40) are shown as sticks. (b) Schematic representation of the sRNA-rpoS-Hfq ternary complex, based on solution data 20. (AAN)4 (green) and U6 (magenta) motifs bind to the distal and proximal faces of Hfq, respectively. The U5 loop in rpoS (orange) interacts with the rim. The complementary regions of the sRNA and mRNA interact with charged residues at the rim, which are needed to initiate base pairing.