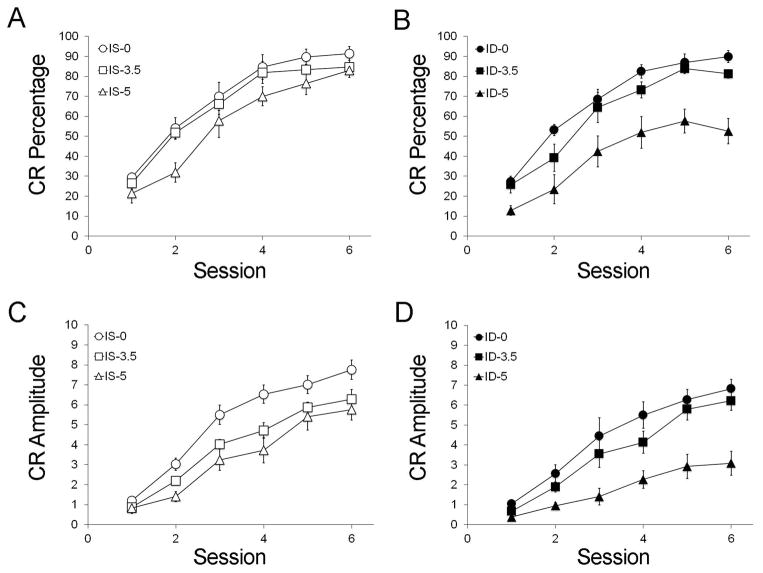
Figure 1.
Delay eyeblink classical conditioning between rats in the iron-sufficient (IS, open symbols, A, C) and iron-deficient (ID, closed symbols, B, D) groups as a function of alcohol dose (○● 0 g/kg, □■3.5 g/kg, △▲5 g/kg). Separately, alcohol and ID significantly affected learning acquisition in terms of conditioned response (CR) percentage (A, B) and amplitude (C, D) during paired training with the CS and US. Animals exposed to the combination of 5 g/kg alcohol and ID were more significantly impaired in acquiring CRs than ID animals exposed to the two lower alcohol doses (n = 9–11 animals per treatment group; error bars represent S.E.M.). Conversely, the impact of 5 g/kg alcohol on learning was drastically mitigated by an iron-sufficient diet.