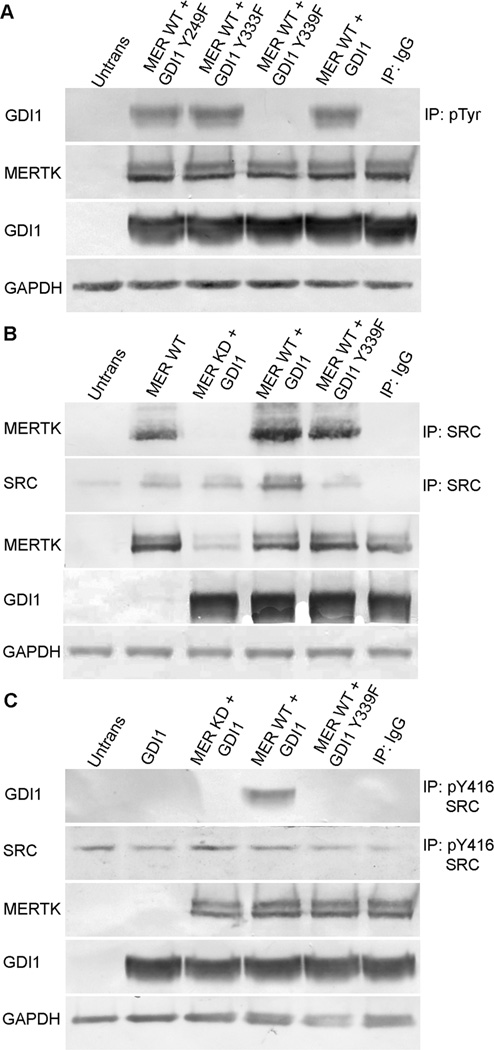
Fig. 5. MERTK, SRC, and GDI1 interaction in transfected HEK-293T cells depends on specific phosphorylation sites in each protein.
Constructs encoding Xpress-tagged wild-type GDI1 or GDI1 tyrosine mutants were co-transfected with wild-type MERTK or a kinase-dead MERTK-R844C mutant, and expression was evaluated in HEK-293T cell lysates by western blotting. (A) Anti-phosphotyrosine immunoprecipitates evaluated for recovery of GDI1 by western blotting using Xpress antibody show that MERTK-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of GDI1 was unaffected for GDI1-Y249F and GDI1-Y333F mutants, but was abolished for GDI1-Y339F. (B) Anti-SRC immunoprecipitates evaluated for recovery of MERTK by western blotting show that SRC associates with wild-type MERTK, but not kinase-dead MERTK, and this association does not require phosphorylation of GDI1. (C) Immunoprecipitates obtained using anti-pTyr416-SRC antibody evaluated for recovery of GDI1 by western blotting with Xpress antibody show that transfections with wild-type MERTK, but not with kinase-dead MERTK, result in association of the activated form of SRC (pTyr416 SRC) with GDI1, but with not the phosphorylation defective mutant GDI1-Y339F. Abbreviations as in Fig. 4; Y249F, GDI1-Y249F; Y333F, GDI1-Y333F; Y339F, GDI1-Y339F.