Fig. 1.
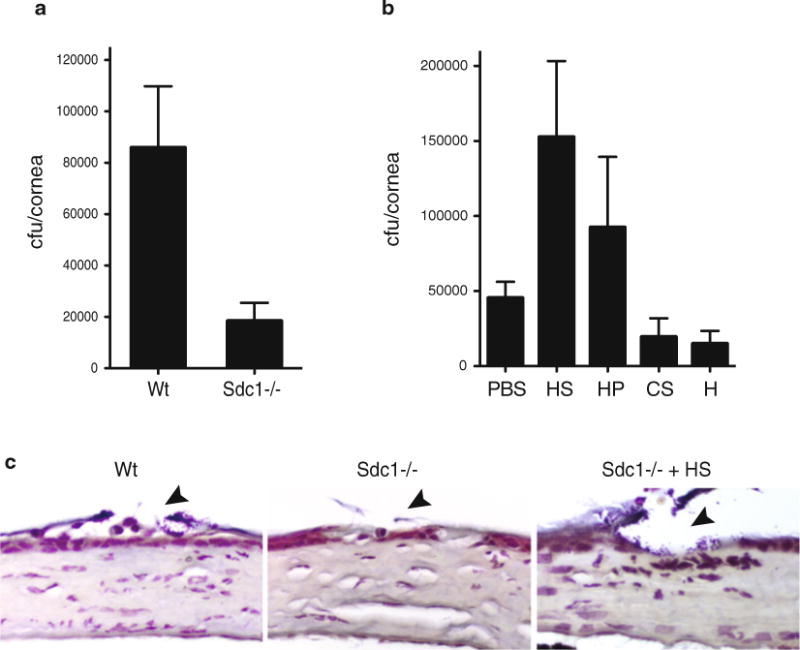
Syndecan-1 promotes S. aureus corneal infection in an HS-dependent manner. (a) Corneas of anesthetized Wt and Sdc1−/− mice on the BALB/c background were scratched with a 29 G needle and infected topically with 1 × 109 cfu of S. aureus strain 8325-4. The corneal bacterial burden was quantified at 10 h postinfection. Data shown are mean ± S.E. (n=9 in Wt and n=6 in Sdc1−/− group). (b) Scarified Wt and Sdc1−/− corneas were infected with 1 × 109 cfu of 8325-4 with or without 200 ng of HS or heparin (HP), or 500 ng of CS-A (CS) or heparosan (H), and the corneal bacterial burden was quantified at 10 h postinfection. Data shown are mean ± S.E. (n=11 in PBS, n=10 in HS, n=7 in HP, n=4 in CS, and n=5 in H group). (c) Paraffin-embedded eye sections of infected Wt and Sdc1−/− mice were Gram stained (arrowhead indicates injured areas). Note the increased number of Gram-positive cocci in Wt cornea infected with S. aureus only and Sdc1−/− cornea co-infected with S. aureus and HS compared to Sdc1−/− cornea infected with S. aureus only
