Fig. 2.
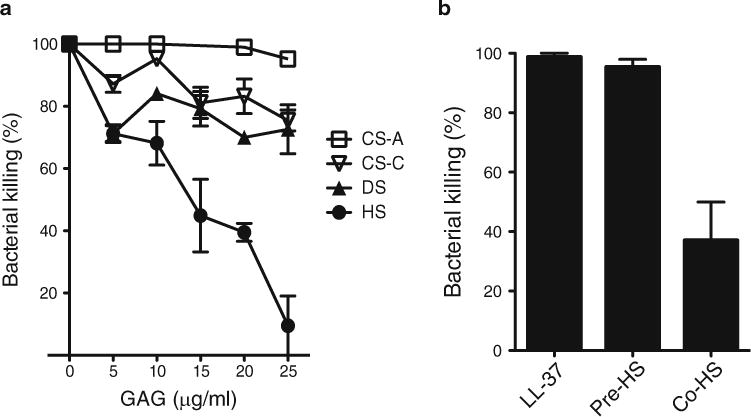
HS specifically inhibits the killing of P. aeruginosa by LL-37. (a) P. aeruginosa (103 cfu) was incubated with LL-37 (3 μg/ml) in 30 μl PBS for 2 h at 37 °C in the absence or presence of increasing doses of CS-A, CS-C, DS, or HS. Bacterial killing was determined by plating out serial dilutions. Data shown are mean ± S.E. (n=4 in each group). Note the significantly increased inhibitory activity of HS at doses ≥15 μg/ml compared to other GAGs. (b) P. aeruginosa was incubated with LL-37 (3 μg/ml) (LL-37 group), preincubated with HS (20 μg/ml) for 30 min, washed free of HS, and then incubated with LL-37 (Pre-HS group), or co-incubated with LL-37 and HS (Co-HS group) for 2 h at 37 °C in a microfuge tube. Bacterial killing was determined by plating out serial dilutions. Data shown are mean ± S.E. (n=4 in each group). This experiment shows that HS does not inhibit LL-37 activity by binding to the bacteria, but rather by directly binding to LL-37 and inhibiting its antibacterial activity
