Figure 2.
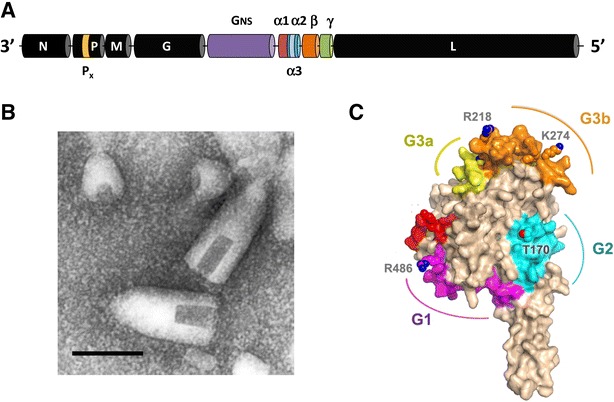
Structure and morphology of BEFV. A Structural organization of the 14.9 kb BEFV genome shown as arranged in negative sense. Structural protein genes (N, P, M, G and L) are shown in black and the various accessory genes are coloured. B Transmission electron micrograph showing BEFV virions and defective-interfering (DI) particles. Scale bar 100 nm. Reproduced from Walker [7] with permission from Springer-Verlag. C Structural model of a monomeric subunit of the BEFV G protein derived by homology modelling using the pre-fusion form of the VSV G protein as a template. The model illustrates the three major neutralization sites (G1, G2 and G3a/b) and amino acid residues shown to be under positive selection in Australia [18]. Adapted with permission from the American Society for Microbiology.
