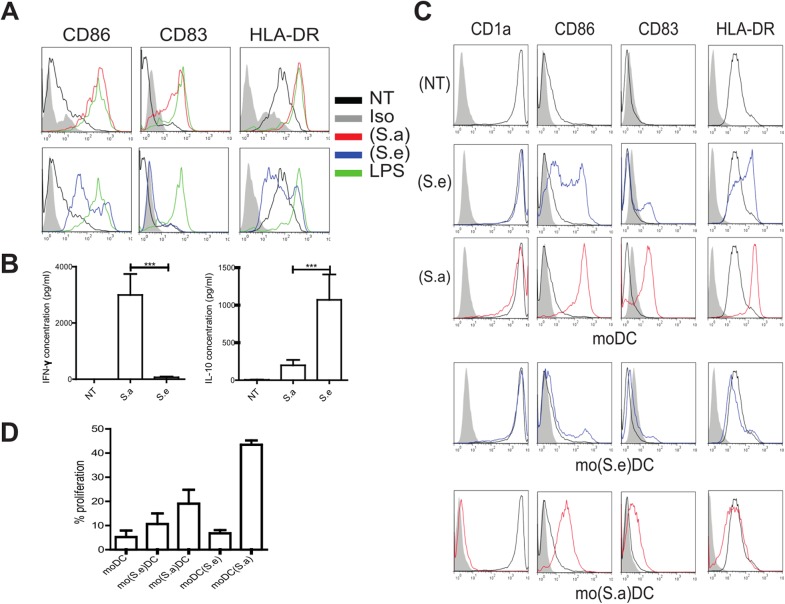
Fig 3. Factors secreted by cutaneous S. aureus and S. epidermidis exert opposite effects on moDC.
(A) Representative activation phenotype (CD86, CD83 and HLA-DR levels) of monocyte-derived dendritic cells (moDC) exposed for 24 hours to the S. aureus (S.a, red) or S. epidermidis (S.e, blue) secretomes obtained from subject P04, or medium (NT, black) or LPS (green). (B) Secreted IFN-γ and IL-10 (pg/ml) levels in moDC as described in (A). Wilcoxon signed-rank test, mean values with SEM are shown, p*** <0.001, N = 14 independent experiments. (C) (S.e) and (S.a) were added to either moDC [moDC(S.e) and moDC(Sa)] or monocytes on day 0 of differentiation (mo(S.e)DC and mo(S.a)DC). (D) Cells were co-cultured with CFSE-labeled allogeneic naïve CD4+ T cells for 5 days at a ratio of 1:10 stimulator to T cells. The percentage of proliferating cells was then determined by flow cytometry. Mean values with +/- SEM are shown, N = 4, one-way ANOVA test p = 0.0009.