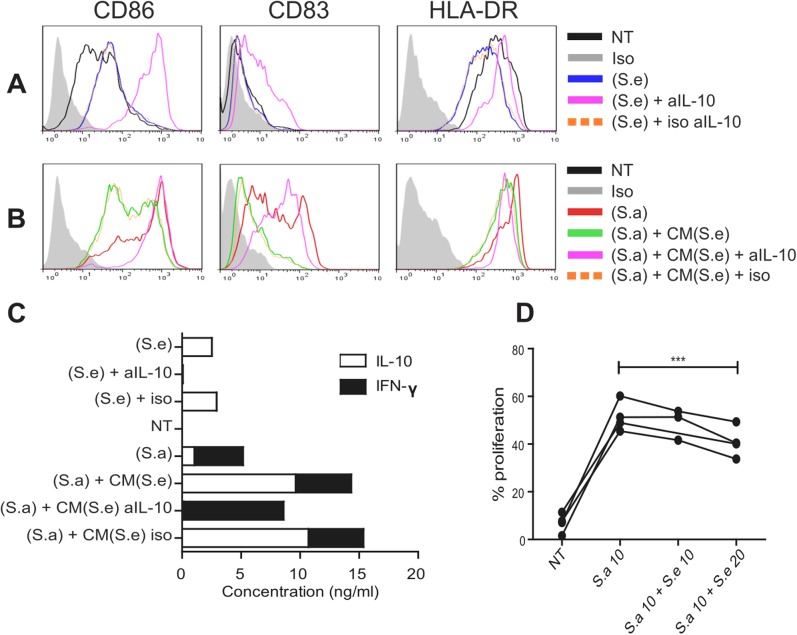
Fig 4. S. epidermidis stimulated moDC release IL-10 that impairs their maturation and reduces S. aureus effect.
(A) Activation profile (CD86, CD83 and HLA-DR levels) of moDC exposed to either medium alone (NT), or the secretomes of S.aureus (S.a) and S.epidermidis (S.e) supplemented with anti-IL-10 or isotype-matched control (iso) antibodies. (B) MoDC were incubated with (S.a) alone or supplemented with conditioned medium (CM) from allogeneic moDC pulsed with (S.e), with the addition of anti-IL-10 or isotype-matched control antibodies. (C) Levels of secreted IFN-γ and IL-10 (ng/ml) by the same moDC presented in (A) and (B). Similar results were obtained in 3 independent experiments. (D) MoDC were exposed to a mixture of (S.a) at m.o.i of 10 (S.a 10) and increasing amounts of (S.e) co-cultured with CFSE-labeled allogeneic CD4+ T cells. The proliferation of T cells was quantified by flow cytometry (%). Paired t-test, p***<0.001 N = 4.