Figure 3.
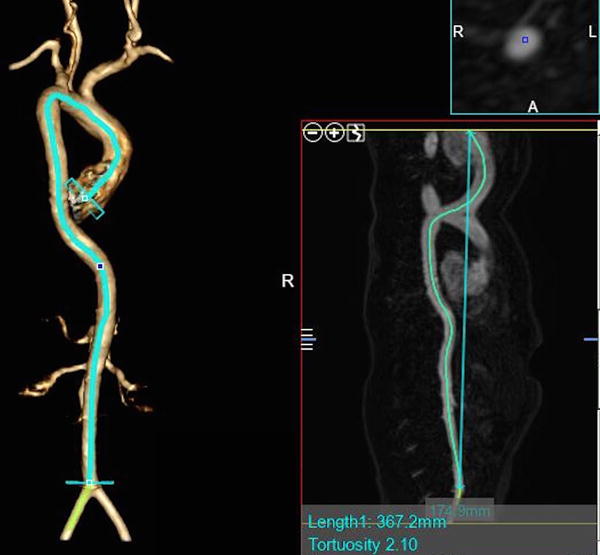
Calculating the aortic tortuosity index (ATI), per Franken et al., International Journal of Cardiology 201529 from a 3D computed tomography angiogram. ATI is calculated as the ratio of aortic length (actual length) to geometric length (straight length). The aortic length (left side of image) was defined as the length of a centerline through the entire aorta (from annulus to aortic bifurcation) created by manually placed seeding points through the lumen of the aorta using post-processing software. Geometric length is the Cartesian distance between its 2 endpoints (added in smaller image on right, overlying the centerline). Aortic tortuosity index (ATI) is measured by dividing aortic length by geometric length. In this example in a patient with significant aortic tortuosity, aortic length = 367.2 mm, geometric length = 174.9 mm, ATI = 2.10. Images complements of Alex Dodd, Texas Children’s Hospital.
