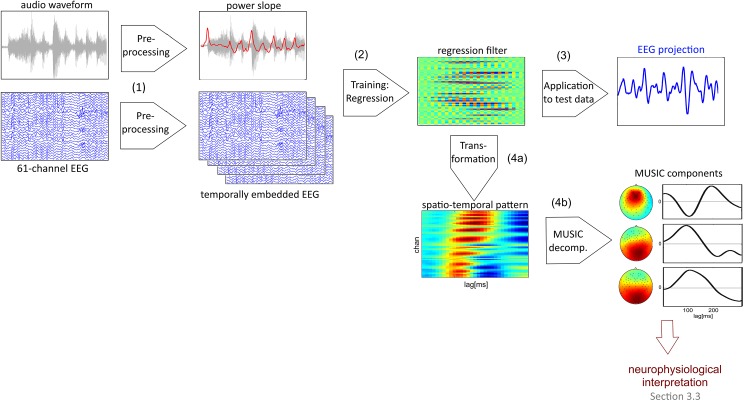
Fig 2. EEG feature extraction.
(1) In the first step of the analysis the 61-channel EEG signal (after generic preprocessing, see Methods) is temporally embedded and the power slope of the audio signal is extracted. In the training step (2) the embedded EEG features are regressed onto the audio power slope (Ridge Regression). After that (3) the resulting spatio-temporal filter (regression weight matrix) reducing the multichannel EEG to a one-dimensional projection is applied to a new presentation of the same stimulus. The regression filter can be transformed (4a) into a spatio-temporal pattern that indicates the distribution of information which is relevant for the reconstruction of the audio power slope. This spatio-temporal pattern, in turn, can be (4b) decomposed into components (derived with the MUSIC-algorithm) which have a scalp topography and a temporal signature. The EEG projections obtained in (3) subsequently are examined with respect to Cortico-Acoustic correlation (CACor).