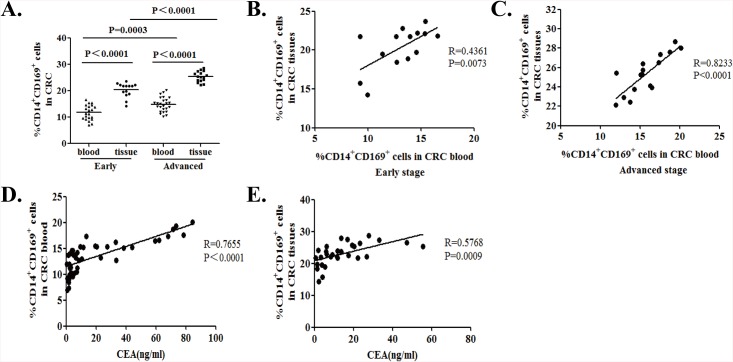
Fig 4. Stratification analysis of the percentages of CD14+CD169+ circulating monocytes and tumor infiltrating macrophages in CRC patients.
The CRC patients were stratified as early (I/II, n = 21) or advanced stage (III/IV, n = 25) and the percentages of CD14+CD169+ circulating monocytes and TIMs in individual patients were analyzed. Furthermore, the potential association between the percentages of CD14+CD169+ circulating monocytes or TIMs and the levels of plasma CEA in individual groups of patients were analyzed. Data are the mean of individual subjects. (A) Percentages of CD14+CD169+ monocytes in PBMCs (n = 21 for early stage, n = 25 for advanced stage of CRC patients) and the percentages of CD14+CD169+ macrophages in TIMs from early (n = 14) or advanced (n = 16) stage of CRC patients. The horizontal lines indicate the median for individual groups. (B) The correlation between the percentages of CD14+CD169+ circulating monocytes and TIMs in early stage of CRC patients. (C) The correlation between the percentages of CD14+CD169+ circulating monocytes and TIMs in advanced stage of CRC patients. (D) The correlation between the levels of plasma CEA and the percentages of CD14+CD169+ circulating monocytes in the CRC patients. (E) The correlation between the levels of plasma CEA and the percentages of CD14+CD169+ TIMs in the CRC patients.