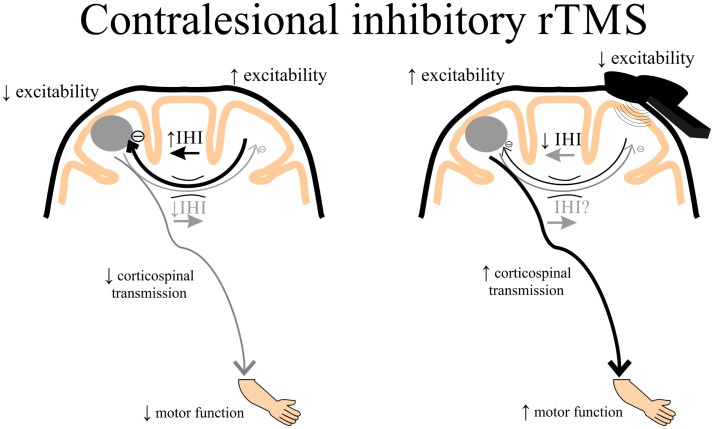
Figure 4.
A schematic of the theoretical effects of inhibitory rTMS over the contralesional cortex. Increased interhemispheric inhibition (IHI) from the contralesional to ipsilesional cortex via the corpus callosum may contribute to decreased ipsilesional corticospinal excitability and diminished motor function of the paretic upper limb. Contralesional inhibitory rTMS may suppress contralesional to ipsilesional IHI and assist in improving ipsilesional corticospinal transmission, potentially leading to better motor function of the paretic upper limb. rTMS, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation.