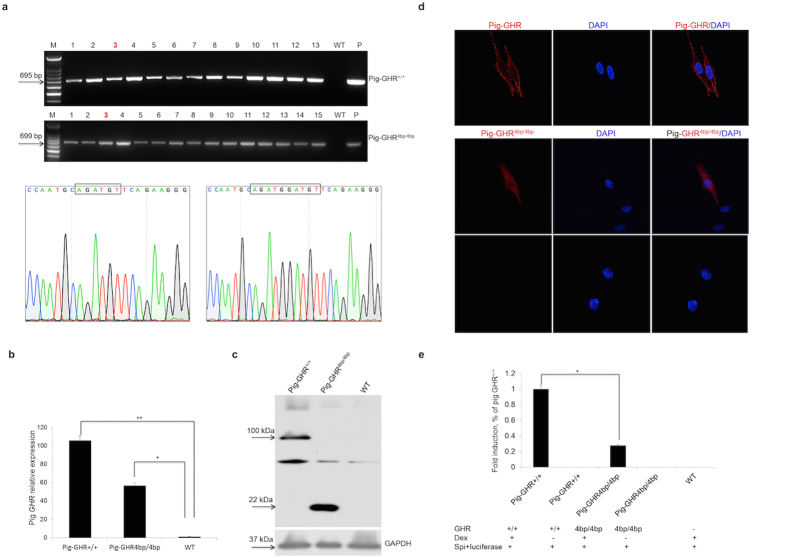
Figure 2. Evaluation of the pig GHR transcript with a 4 bp insert in vitro.
(a) RT-PCR of the 4 bp insert and the wild-type pig GHR transcripts in stably integrated DF1 cell clones. Pig-GHR+/+ and Pig-GHR4bp/4bp represent the wild-type and the 4 bp insert pig GHR, respectively; numbers represent the different cell clones obtained; WT represents the results obtained from un-transfected DF1 cells; P represents the plasmid control; and the sequencing results of the clones are also shown. (b) qRT-PCR of pig GHR mRNA expression in stably integrated DF1 cells. The expression levels were determined by the expression relative to GAPDH (an internal control). The data were combined from three independent experiments; the bars represent the means ± SD (n = 4–6 cell clones per group); **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05. (c) Western blot of pig GHR expression in stably integrated DF1 cells. The wild-type and mutated GHR are 100 kDa and 22 kDa, respectively; GAPDH was used as an internal control. (d) Determination of the localization of pig GHR in DF1 cells. Stably transfected DF1 cells were stained with the anti-Flag tag primary antibody (1:500) and Cy3-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG antibody. DAPI (blue) staining indicates the nucleus. The data are representative of at least three independent experiments. Images were obtained with a 100x oil objective lens. (e) Dual-luciferase assay of the mutated pig GHR and the wild-type GHR. Dex represents Dexamethasone (200 nM); Spi+luciferase is the reporter vector used in this assay; GH (50 nM) was used to induce the signal transduction; the bars represent the means ± SD; *P < 0.05.