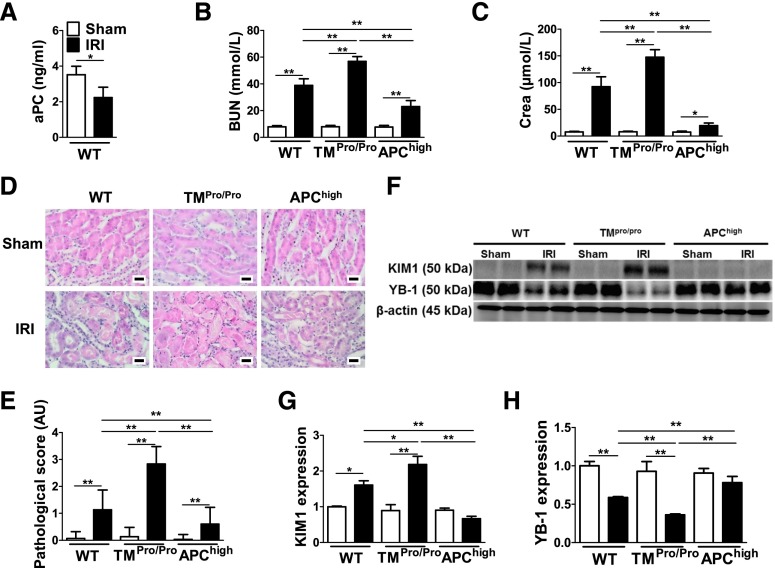
Figure 1.
Protection from renal IRI by TM-dependent PC activation is associated with sustained YB-1 expression. (A) Plasma levels of aPC are reduced in WT mice after renal IRI (black bars) compared with control (sham, open bars) mice. BUN (B) and creatinine (Crea) (C) in control (Sham) (open bars) and experimental (IRI) (black bars) WT, TMPro/Pro, and APChigh mice. Exemplary images of H&E-stained kidney section from WT, TMPro/Pro, and APChigh mice without (Sham) or with IRI (D) and a bar graph summarizing results of pathologic scores (E). TM-dependent PC activation modulates KIM1 and YB-1 expression during renal IRI in vivo; representative immunoblots (F) and bar graphs summarizing results [(G) and (H)]. Mean±SD values of at least six mice per group [(A)–(C), (E), (G), and (H)]; size bar: 20 µm (D); *P<0.05; **P<0.01 [(A): t test; (B), (C), (E), (G), and (H): ANOVA]. H&E, hematoxylin and eosin.