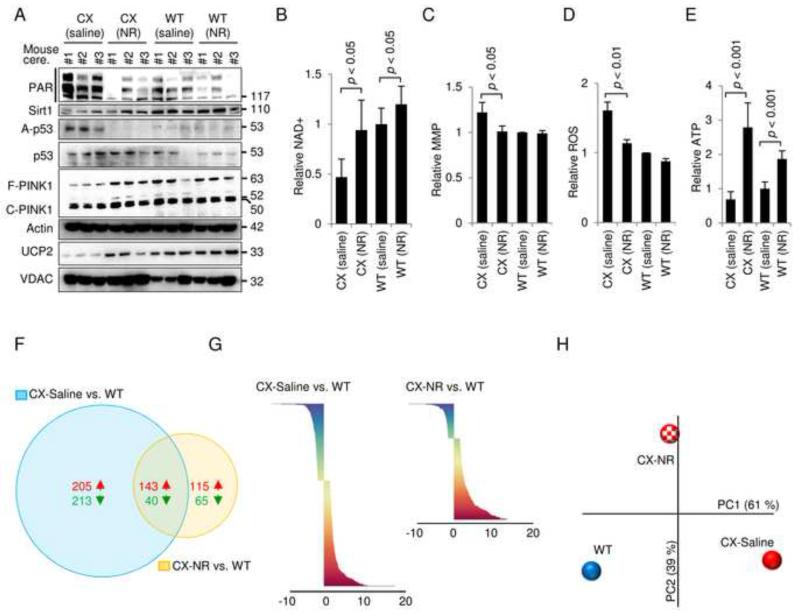
Figure 7. The NAD+ precursor nicotinamide riboside can rescue the mitochondrial phenotype of CX mice in vivo.
(A) Immunoblot of cerebellar proteins in 3-month old WT and CX mice treated with saline or nicotinamide riboside (NR) subcutaneous injections for 2 weeks (500 mg NR/kg body weight). Each lane is a separate mouse. (B) NAD+ levels in the cerebellum of the mice described in (A) (means ± S.D., n=4). (C) The mitochondrial membrane potential of isolated cerebellar mitochondria from mice described in (A) (means ± S.D., n=4). (D) ROS production in isolated cerebellar mitochondria from mice described in (A) (means ± S.D., n=4). (E) ATP levels in the cerebellum of mice as described in (A) (means ± S.D., n=4). (F) Venn diagram of significantly changed gene in the cerebellum when comparing CX-saline with WT-saline and CX-NR treated with WT-saline treated (n=3). (G) An overview of the significantly changed genes when comparing CX-saline vs WT-saline and CX-NR vs WT-saline (n=3). (H) Principal component analysis of the average Z-scores of all the genes in each group (n=3).