Table 1.
Model parameter estimates using the ocular-serum TMDD model
| Parameter | Symbol (unit) | Estimate | RSE (%) | 95% CI | Shrinkage (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| Ocular parameters | ||||||
| Ocular elimination rate constant of druga | kout (1/day) | 0.117 | 1.25 | 0.111 | 0.123 | |
| Ocular elimination rate constant of complex | koutC (1/day) | 0.135 | 1.54 | 0.127 | 0.144 | |
| Ocular influx/synthesis rate constant of target | kinT (µg/mL/day) | 0.364 | 0.635 | 0.360 | 0.369 | |
| Correction factor for drug:target molar ratio and assay differencesc | λA | 2.23 | 27.7 | 1.440 | 3.46 | |
| Vitreous volume of distribution | VVITR (mL) | 3.09 | 3.24 | 2.88 | 3.23 | |
| Ocular degradation/elimination rate constant of drug target | koutT (1/day) | 0.27 | 0.935 | 0.236 | 0.276 | |
| Vitreous-aqueous partition coefficient of drug | λAQ | 13.0 | 0.586 | 12.7 | 13.4 | |
| Systemic parameters | ||||||
| Systemic volume of distribution | Vc (mL) | 2410 | 0.0658 | 2390 | 2440 | |
| Systemic elimination rate constant of druga | k (1/day) | 1.89 | 6.53 | 1.74 | 2.05 | |
| Quasi-steady rate constantd | Kss (µg/mL) | 0.96 × 10−3 (fixed) | ||||
| Covariates | ||||||
| Power for age effect on kout | Θage-kout | −0.770 | 45.5 | −1.45 | −0.0831 | |
| Power for age effect on k | Θage-k | −1.63 | 23.5 | −2.38 | −0.877 | |
| Multiplier for sex effect on k | Θsex-k | 0.739 | 21.1 | 0.652 | 0.837 | |
| Variability | ||||||
| Intersubject variability for ocular clearance | 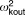 |
27.3% | 19.1b | 21.6% | 32.0% | 6.3 |
| Intersubject variability for correction factor | ω2λA | 59.1% | 38.0b | 29.8% | 78.0% | 0.8 |
| Intersubject variability for systemic clearance | 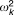 |
27.5% | 23.8b | 20.1% | 33.3% | 20.7 |
| Residual error for aqueous measurements |
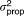 , AQ , AQ
|
25.8% | 28.3b | 17.2% | 32.2% | |
| Residual error for serum measurement |
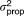 , SER , SER
|
32.9% | 10.1b | 29.5% | 36.1% | |
CI, confidence interval; RSE, relative standard error.
For a typical 80-year-old male patient.
RSE for variances.
Ratio of the molecular weights of the drug and the target is equal to 2 (within 95% CI of the estimated value). Minor difference with the estimated value could be due to assay differences or differences in volumes of distributions of the drug and the target.
