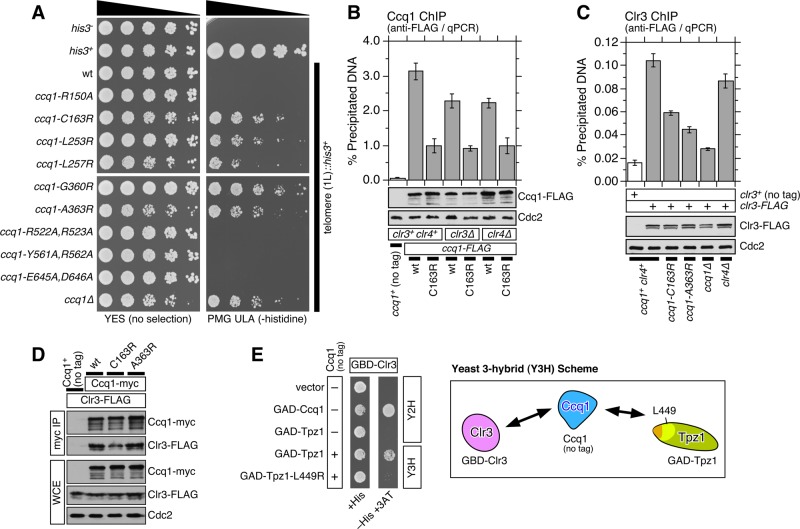
FIGURE 6:
Ccq1-Tpz1TPP1 interaction contributes to heterochromatin formation and localization of the SHREC subunit Clr3 to telomeres. (A) Effects of Ccq1-Tpz1TPP1 interaction disruption mutants on transcriptional silencing of his3+ marker inserted adjacent to telomeric repeats (Nimmo et al., 1998). A fivefold serial dilution series of indicated strains was spotted on YES or PMG ULA (−histidine) plates. (B and C) Effects of disrupting Ccq1-Tpz1TPP1 interaction and elimination of factors essential for heterochromatin formation on telomere association for (B) Ccq1 or (C) Clr3, monitored by ChIP assays. Error bars represent SEM from at least four experimental replicates for Ccq1 and at least three experimental replicates for Clr3. Statistical analysis of ChIP data by two-tailed Student’s t test is shown in Supplemental Table S4. Expression levels of FLAG-tagged Ccq1 or Clr3 were monitored by Western blot analysis. Anti-Cdc2 blots served as loading control. (D) Examination of Ccq1-Clr3 interaction by co-IP indicated that Ccq1-Tpz1TPP1 interaction is dispensable for Ccq1-Clr3 interaction. (E) Y3H assay for Clr3, Ccq1, and Tpz1. Expression of Ccq1 was able to bridge interaction between GBD-Clr3 and GAD-Tpz1 to allow growth on plates that lacked histidine (−His) and contained 1 mM 3AT. As expected, disruption of Ccq1-Tpz1TPP1 interaction by tpz1-L449R mutation eliminated positive Y3H signal.