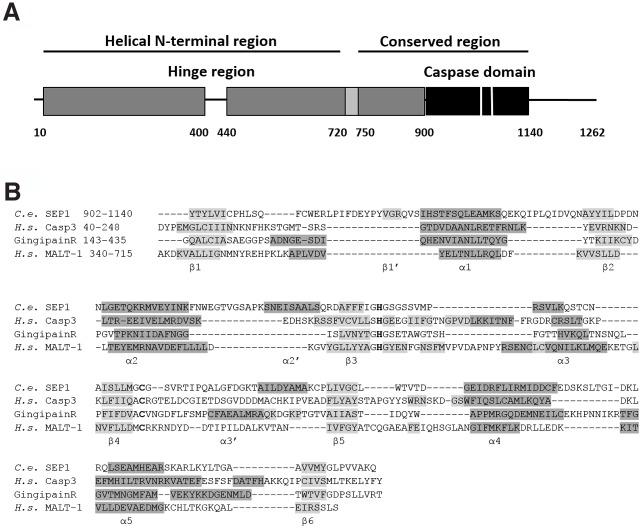
Fig 1. Separases from all species share a similar topology with highly conserved regions, which includes a caspase-like domain in their C-terminal region.
(A) Consolidated secondary structure prediction of separase from C. elegans using both PsiPred and JPred predicts a largely helical N-terminus (dark grey) with an unstructured region around residue 400 and a region of three β-strands from residues 720 to 750 (light grey). The conserved C-terminal half harbours the caspase-like domain (black), residues 900 to 1140. The catalytic dyad is indicated as white lines. (B) Multiple sequence alignment of the caspase-like domain of separase from C. elegans in comparison with human caspase 3, gingipain-R and MALT-1. Alignment was manually adjusted using Jalview to match secondary structure elements from predictions (PsiPred) of separases to structural elements as observed in caspase 3 (3EDQ), MALT-1 (3UO8) and gingipain R (1CVR). α-helices are shown in dark grey and β-strands in light grey. The conserved catalytic dyad (C, H) is shown in bold letters.