Fig 2. Comparison of the structures of human caspase 3, human MALT-1 and gingipain-R.
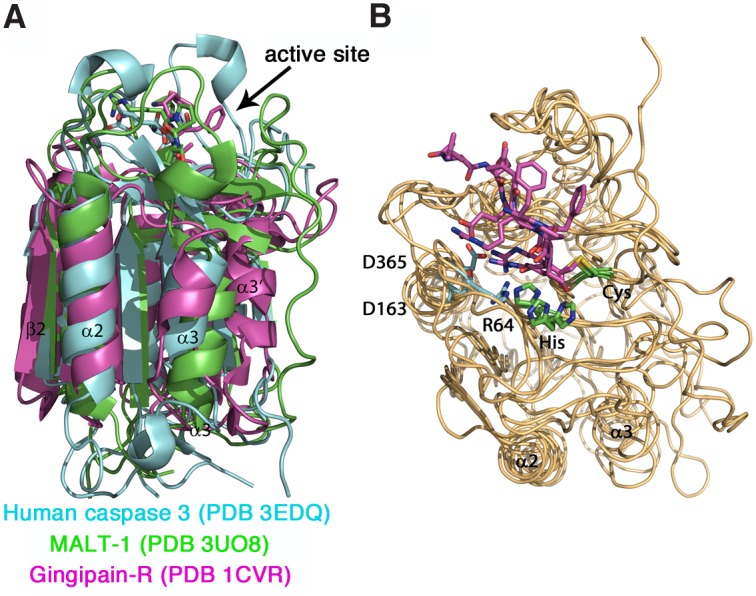
(A) Overlaid structures of human caspase 3 (cyan, PDB code 3EDQ), human MALT-1 (green, PDB code 3UO8) and gingipain-R (magenta, PDB code 1CVR) show a similar overall fold consisting of a central six-stranded β -sheet flanked by α-helices. In gingipain-R, a helix connects the first four with the last two β-strands and replaces the inter-subunit linker present in caspases. In caspases the first four β -strands belong to the larger subunit p20 and the remaining two β-strands to the smaller subunit p10. The C-terminal Ig domain of MALT-1, subdomain A and the C-terminal IgSF domain of gingipain-R were omitted for clarity. (B) Comparison of the substrate binding pockets reveal a very similar binding mode of peptide inhibitors ace-LDESD-cho (for caspase 3), z-VRPR-fmk (MALT-1) and FFR-cmk (gingipain-R). Peptide inhibitors (magenta) and catalytic residues His and Cys (green) are shown as sticks. Residues mainly responsible for the recognition of the respective peptide P1 are shown as cyan sticks: Arg64 (for caspase 3), Asp163 (for gingipain-R) and Asp365 (for MALT-1). Figures were prepared with PyMol.
