Fig 3. Homology modelling of the caspase-like domain of C. elegans separase using caspase 3 as template.
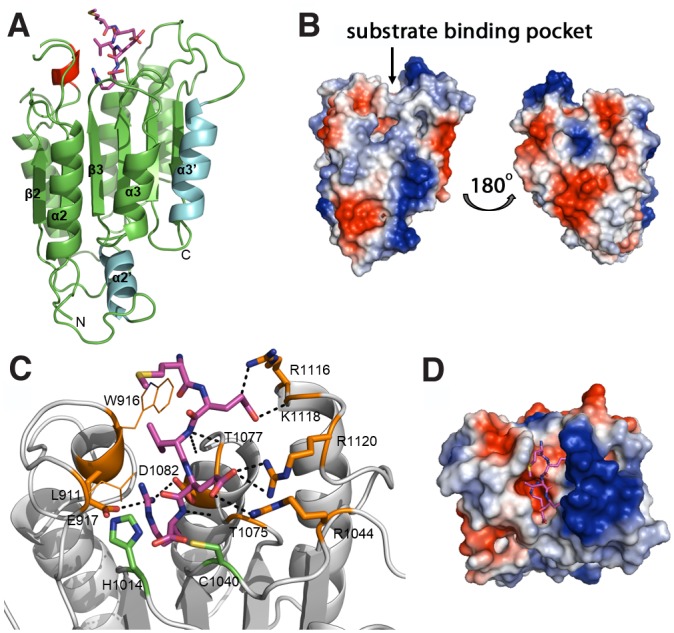
(A) The homology model of the caspase-like domain of separase from C. elegans is shown in cartoon view with the proposed substrate peptide MEVER as sticks (magenta). The additional helices α2’ and α3’ that were introduced into the caspase 3 template (cyan) as well as the short helix modelled into the loop between β1 and α1 (red) are highlighted. Core model and loops were generated using MODELLER and energy minimized using GROMACS. (B) Surface electrostatics of the caspase-like domain in separases (shown here without substrate peptide) shows several positive (blue) and negative (red) patches that may be important for interactions with modulators such as securin or other domains within separase itself. Left: front view, same as view in (A). Right: view from back of molecule via vertical rotation by 180°. (C) Proposed interaction of the separase active site with substrate peptide MEVER (in sticks, magenta). Residues interacting with the peptide are labelled and shown in orange. Hydrogen bonds formed between peptide and protein are shown as black dashes. The catalytic residues H1014 and C1040 are indicated as green sticks. (D) Electrostatic properties of the substrate pocket reveal a deep negative pocket that receives the P1-Arg residue and a large positive patch that locks the side chains of P2-Glu and P4-Glu in place. All figures were prepared using PyMol.
