Fig 4. Interactions made between the predicted substrate peptide MEVER and the homology model of the C. elegans separase caspase domain.
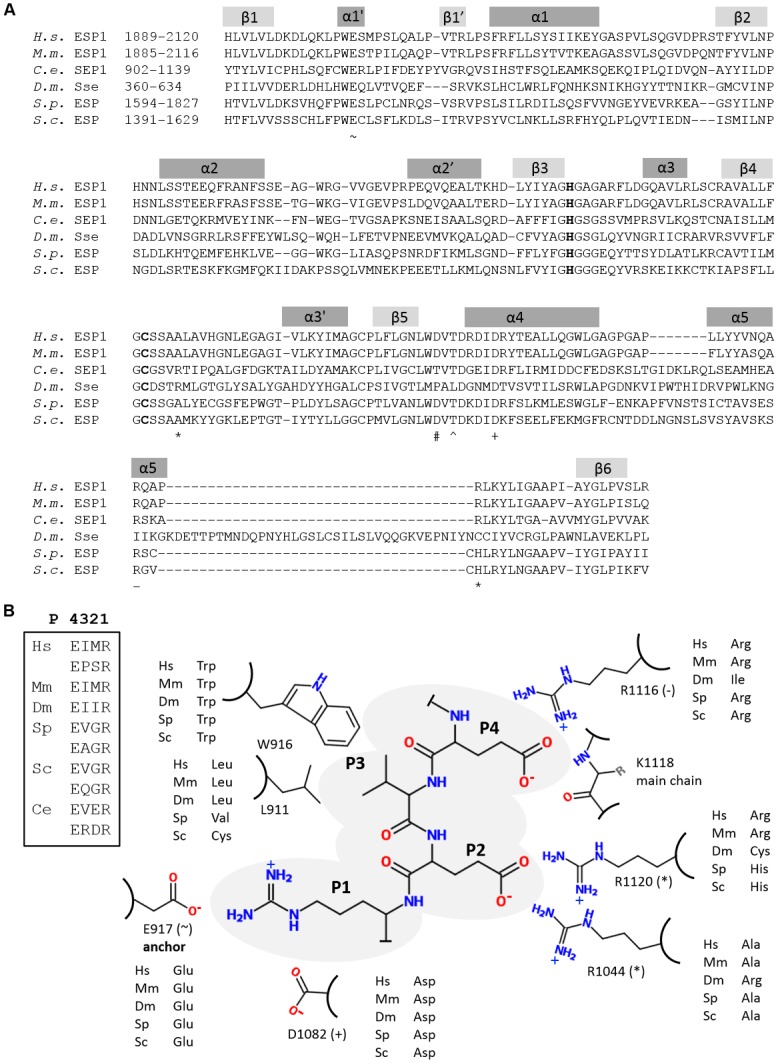
(A) Residues in separases that interact with the substrate peptide are highlighted in an alignment. P1-Arg is anchored via hydrogen bonds to Glu917 (~) and Asp1082 towards the N-terminus of helix α4 (+). The main chain amide-NH of residue P1 interacts with main chain oxygen atom of Thr1075 (#). The side chain of P2-Glu forms hydrogen bonds to Arg1120 (which is located in a well-conserved region preceding β6) and Arg1044 (which is located in a loop region between helix α3’ and β4) which are both highlighted with * in the alignment. Aside from hydrophobic interactions, P3-Val interacts with both the main chain and side chain oxygen atoms of Thr1077 (^). P4-Glu forms hydrogen bonds to the main chain amide of Lys1118 and guanidino group of Arg1116 (–). α-helices are shown in dark grey and β-strands in light grey. The catalytic dyad (C, H) is shown in bold letters. (B) Schematic representation of interactions between C. elegans separase and the proposed substrate peptide EVER. Corresponding interacting residues in separases from other species are taken from Fig 4A. Core recognition sites of Scc1 proteins are shown in the boxed inset.
