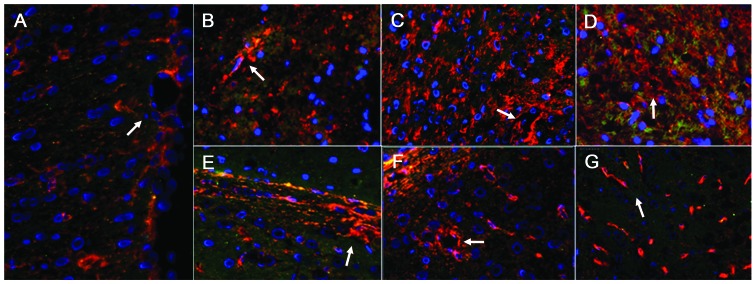
Figure 5.
AQP4 distribution in double-labeled immunofluorescence images of the damaged area and contralateral non-damaged area of the brain (magnification, ×1.7). (A) Images from the sham operation rats. (B–D) Images from the damaged side of the brain at 6, 24, and 72 h, respectively. (E–G) Images from the contralateral non-damaged side of the brain at 6, 24, and 72 h, respectively. The expression of AQP4 appeared red, the stained glial fibrillary acidic protein (a glial cell indicator) appeared green, and stained nuclei of glial cells appeared blue. In the sham operation group, AQP4 was predominantly expressed in the glial cells, vascular endothelial cells and the podocytes of the glial cells (white arrow in A). In the damaged area, glial cells exhibited abundant expression of AQP4 after 6 h (white arrow in B), and after 24 h and 72 h, the blood vessels and glial cells exhibited significant AQP4 expression (white arrow in C and D). In the contralateral non-damaged area, the expression of AQP4 in the glial cells increased after 6 h (white arrow in E); AQP4 was abundant in the blood vessels and glial cells after 24 h and 72 h (white arrows in F and G), which was higher in the glial cells. AQP4, aquaporin 4.