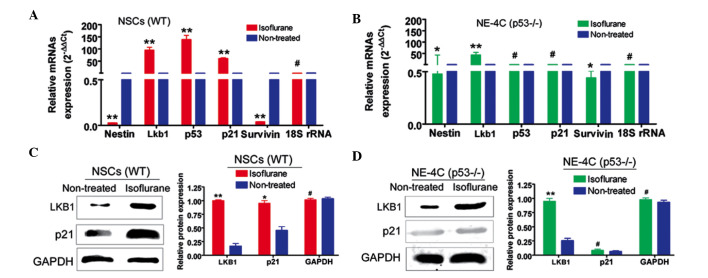
Fig. 2.
Isoflurane activates Lkb1-p21 signalling in WT NSCs, although not in NE-4C (p53−/−) cells. (A) RT-qPCR analysis reveals that the mRNA expression levels of Lkb1, p53 and p21 in WT NSCs treated with an IC50 concentration of isoflurane were significantly higher compared with that in untreated cells (**P<0.01; #P>0.05 compared with the non-treated group; n=3). (B) RT-qPCR analysis indicates that the mRNA expression levels of p53 and p21 in isoflurane-treated NE-4C (p53−/−) cells were unchanged compared with the untreated cells (**P<0.01; *P<0.05; #P>0.05 compared with the non-treated group; n=3). (C) Western blotting indicates that the protein expression levels of Lkb1 and p21 in isoflurane-treated WT NSCs were significantly increased compared with untreated cells (**P<0.01; *P<0.05; #P>0.05 compared with the non-treated group; n=3). (D) Western blotting indicates that only the protein expression level of Lkb1 was increased in isoflurane-treated NE-4C (p53−/−) cells (**P<0.01; #P>0.05 compared with the non-treated group; n=3). GAPDH was used as a loading control. RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; WT NSCs, wild-type neural stem cells.