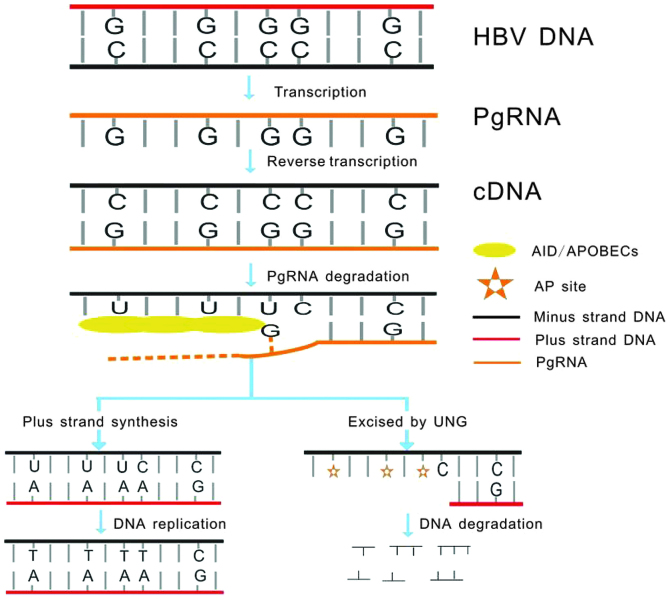
Figure 1.
HBV DNA is transcribed to pgRNA as a replicative RNA intermediate, according to which the minus DNA strand (cDNA) forms. ssDNA is formed as the pgRNA is degraded. AID/APOBECs catalyze cytosine deamination of HBV DNA on the cDNA, producing uracil during reverse transcription. Uracils in DNA (including cccDNA) are recognized and excised by UNG leading to formation of AP sites. These AP sites are recognized by cellular AP endonucleases leading to DNA digestion. The HBV DNAs that do not undergo degradation, generate C-to-T transitions in minus strand DNA and G-to-A transitions in plus strand DNA during general DNA replication. HBV, hepatitis B virus; pgRNA, pregenomic RNA; ssDNA, single stranded DNA; AID, activation-induced cytidine deaminase; APOBEC, apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like; cccDNA, covalently closed circular DNA; UNG, uracil DNA glycosylases; AP, apurinic/apyrimidinic.