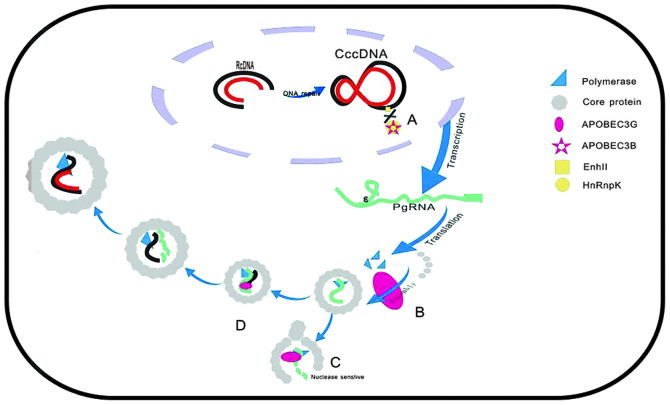
Figure 2.
The rcDNA genome is converted into cccDNA by cellular repair factors. Then, the cccDNA is transcribed to the pgRNA and subgenomic mRNAs (not shown). The mRNAs are transported to the cytoplasm. The pgRNA is translated in the cytosol to form HBV core protein and the viral polymerase. These three components assemble to form the core particle. The first (minus) DNA strand forms within the core particles via reverse transcription of the pgRNA to DNA; the pgRNA is degraded by viral RNase H as the plus strand is synthesized. (A) A3B inhibits the binding of HnRnp K to the Enh II of HBV; (B) A3G may inhibit pgRNA packaging; (C) A3G renders HBV core protein-associated full-length pgRNA nuclease-sensitive; (D) A3G blocks DNA strand elongation and targets a DNA-RNA hybrid. rcDNA, relaxed circular DNA; cccDNA, covalently closed circular DNA; pgRNA, pregenomic RNA; HBV, hepatitis B virus; APOBEC, apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like; HnRnp K, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K; Enh II, enhancer II.