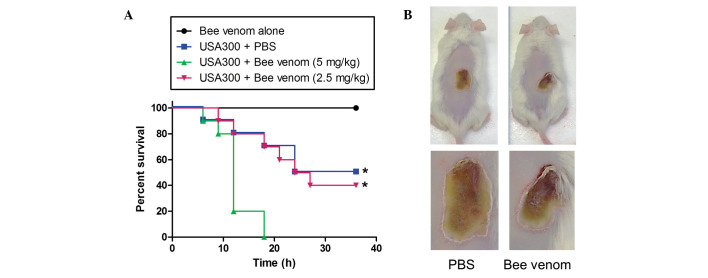
Figure 4.
Protection against MRSA infection by bee venom. (A) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of mice inoculated with the MRSA USA300 strain. Staphylococcus aureus USA300 (0.5×108 CFU/ml) in 0.1 ml PBS was injected i.p into CD1 male mice (n=10 per group). After 1 h, bee venom (2.5 or 5 mg/kg) in 0.1-ml sterile PBS buffer was also injected i.p. Survival rates were monitored every 3 h for 36 h. *P<0.001. (B) Images of the mice were captured 10 days after skin infection by the USA300 strain. The mice were administered with 106 CFU USA300 in PBS subcutaneously, and bee venom (100 µg in 80 µl) or sterile PBS was applied to the surface of the skin infection once each day. Lesion progression was examined every day for 10 days, and lesion dimensions were measured daily using callipers. MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; i.p, intraperitoneally.