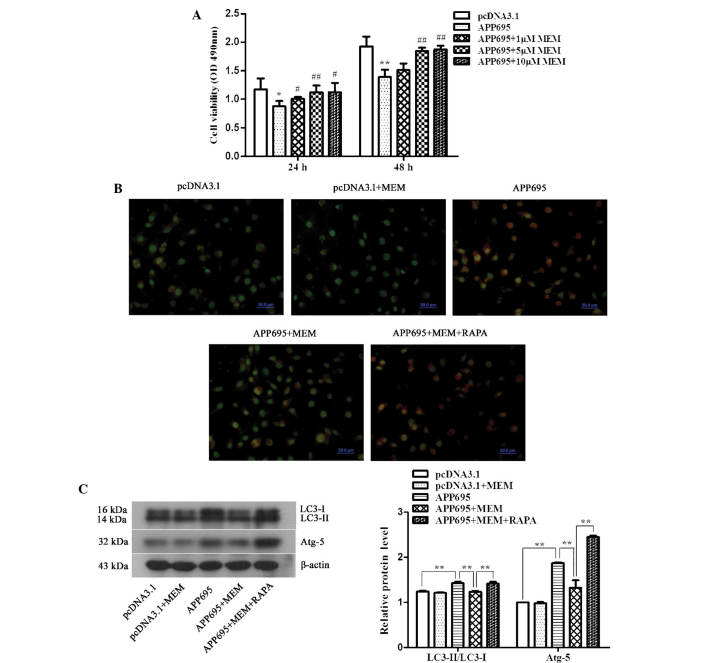
Figure 2.
Increase in neuronal cell viability and inhibition of cell autophagy in the Alzheimer's disease cell model following treatment with memantine. (A) Detection of cell viability using an MTT assay. Cells were inoculated onto 96-well plates and treated with 1, 5 or 10 µM memantine. The absorbance values (OD, 490 nm) of the cells from each group were measured at 24 and 48 h. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01, vs. the pcDNA3.1 group; #P<0.05 and ##P<0.01, vs. the APP695 group. (B) Detection of autophagosomes using acridine orange staining. The cells were inoculated onto coverslips in 12-well plates. Following treatment with the indicated drugs for 24 h, the cells were stained with 0.01% acridine orange. The results were observed under a laser scanning confocal microscope (magnification, ×400; scale bar, 50 µm), and the most representative images are shown. Normal cells exhibit green fluorescence and autophagosomes exhibit orangered fluorescence. (C) Detection of LC3-II/LC3-I and ATG5 protein expression levels as determined by western blot analysis. β-actin was used as an internal control. Representative results from three experiments repeated in triplicate are shown. **P<0.01. All of the above experiments were repeated in triplicate and all values are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Groups: pcDNA3.1, cells transfected with empty vector; APP695, cells transfected with APP695 overexpression vector; memantine, cells treated with 5 µM memantine for 24 h; RAPA, cells were pre-treated with 0.2 µM RAPA for 24 h prior to treatment with memantine. LC3, protein light chain 3; ATG-5, autophagy protein 5; OD, optical density; APP695, β-amyloid precursor protein with 695-amino-acid mutation; RAPA, rapamycin.