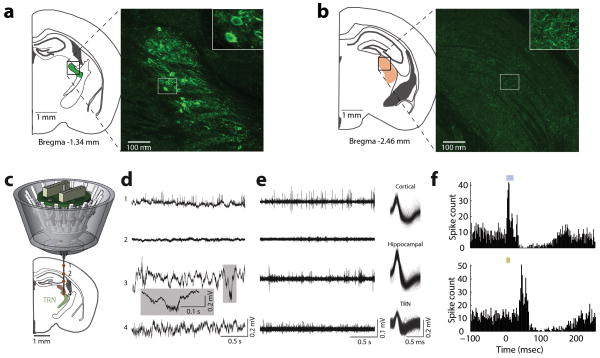
Extended Data Figure 5. Independently adjustable, multi-electrode recording of visTRN neurons.
(a, b) Injection of retro-lenti-DIO-ChR2-EYFP into LGN labels visTRN neurons but not LGN interneurons. (a) Histological image is maximal projection of four 2μm confocal planes showing labelling of visTRN neurons (Inset: zoom in showing cell bodies). (b) Image as in (a), but from LGN of the same animal (Inset: zoom in showing terminals). (c) Schematic of independently adjustable multi-electrode drive. (d) Example activity recorded from different depths during adjustment. Distinct patterns of physiological activity are observed along the trajectory in the broadband LFP signal (0.1Hz–32KHz). (e) Highpass filtered signals (600Hz–10kHz) showing spiking activity with isolated, clustered units showing distinguishable waveform characteristics in distinct structures. (f) Example PETH of ChR2 mediated visTRN response to laser activation (top, 473 nM ~4mW stimulation, 20 ms) and to visual stimuli (bottom, 10 ms pulse).