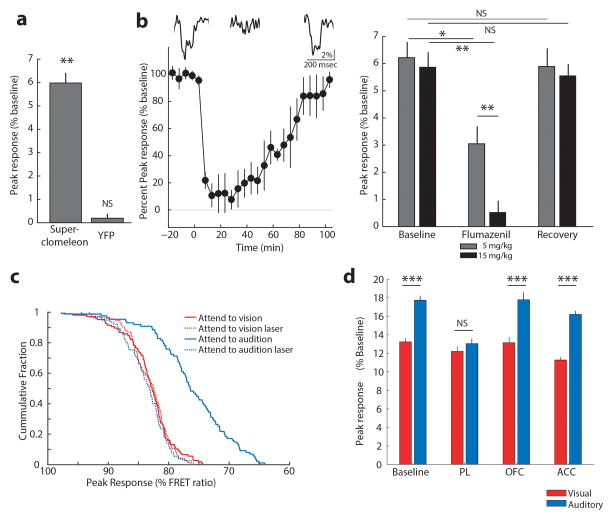
Extended Data Figure 10. Light-evoked fast chloride photometry transients measured in LGN are GABAa receptor dependent and sensitive to visTRN and PL inactivation in the cross-modal task.
(a) Peak superclomeleon FRET and YFP control responses to light stimuli (50ms, 0.1 Hz) delivered to the eye contralateral to the recorded LGN (n > 90 trials from 3 mice for superclomeleon and from 4 YFP mice, *** p<0.001, Friedman Test). (b) Chloride photometry transients are sensitive to GABAa receptor antagonist flumazenil in a dose-dependent manner. Left Injection of 15 mg/kg (i.p.) resulted in a 90% peak reduction of light evoked chloride photometry responses that recovered over the course of 90–100 min as predicted by flumazenil pharmacokinetics. Insets show example traces of single events recorded during baseline, peak suppression and recovery. Right Quantification of the maximal suppressive effects and recovery of 5 and 15 mg/kg flumazenil on chloride photometry responses (n > 90 trials from 3 mice, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, Friedman Test). (c) Cumulative distributions of unitary visual evoked superchlomeleon FRET peaks in response to light stimuli in the cross-modal task. Under baseline conditions, ‘attend to audition’ trials exhibited significantly larger amplitudes than ‘attend to vision’ trials, consistent with average data in Fig 5f. Optogenetic silencing of visTRN eliminated the difference between trial types and resulted in peak amplitudes comparable to baseline ‘attend to vision’ trials (n = 3 mice, p < 0.005 for ‘attend to audition’ trials vs. all other trial types, Kolmogorov-Smirnov statistics with Bonferroni correction). (d) Combined optogenetic inactivation of different frontal cortical regions and chloride photometry in LGN while mice perform the cross-modal task. Only PL inactivation eliminates differential inhibition between visual and auditory trials (n = 6 mice, *** p<0.001, Wilcoxon Rank-Sum Test).