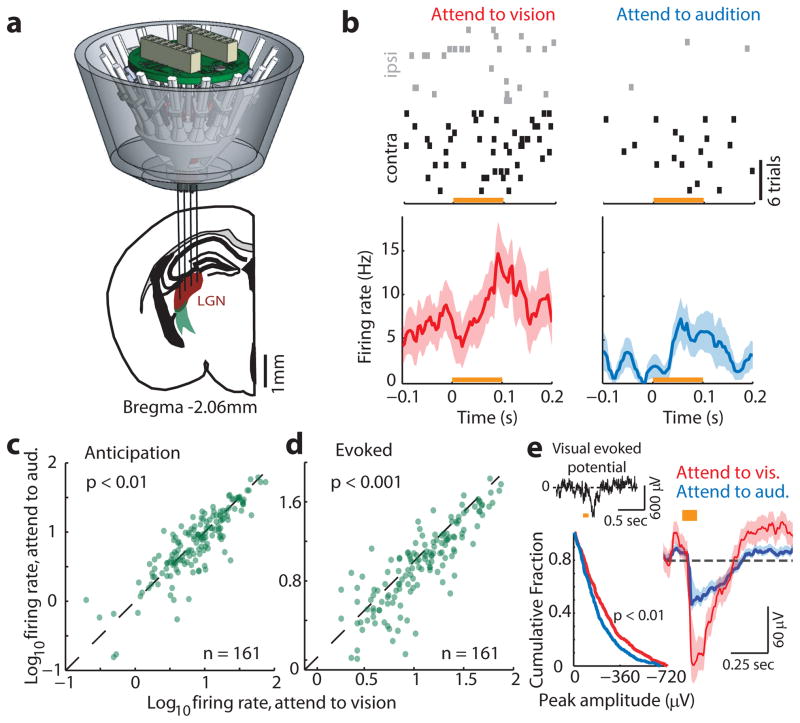
Figure 4. Direct evidence for visual thalamic gain modulation in divided attention.
(a) Cartoon depiction of multi-electrode targeting of LGN in freely behaving mice. (b) Example of differential modulation of a single LGN cell spiking under the two anticipatory task conditions. Note that contralateral eye stimulation (with respect to recording electrodes) resulted in more robust visual drive. More importantly, the cell discharged more spikes during anticipation and presentation when attention was directed towards vision. (c–d) Group analysis of phenomenon in b (n = 161 cells, 4 mice, Wilcoxon rank-sum test). (e) Enhanced visual responses were similarly observed at the level of visual evoked potentials (top left, example VEP; bottom left, cumulative distribution of VEP amplitudes, showing higher values for ‘attend to vision’ trials (p < 0.01, KS test). Right, average VEP from 4 mice (684 visual and 633 auditory trials from 29 sessions), shaded errors are 95% confidence intervals.